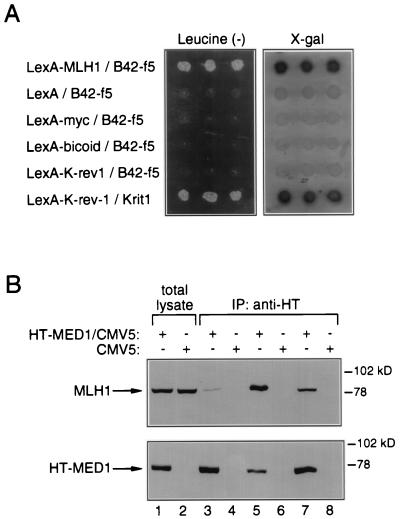
Figure 1.
Interaction between f5/MED1 and MLH1. (A) Specific association of f5 and MLH1 by yeast interaction trap. EGY191 cells were cotransformed with various combinations of plasmids, as indicated, along with the lacZ reporter pSH18–34. Individual transformants were replated onto Leu (−)/galactose plates to score for activation of the LEU2 reporter (Left) and onto X-Gal/galactose plates to score for activation of the lacZ reporter (Right). All interactions were galactose-specific. K-rev-1 and Krit1 represent a positive control for interaction. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of MED1 and MLH1 from human cells. A band reacting with the anti-MLH1 antibody and comigrating with MLH1 is detected by Western blotting in antihemagglutinin immunoprecipitates from HT-MED1/CMV5-transfected HEK-293 cells and not from CMV5-transfected control cells (Upper). Western blotting of a parallel gel with the antihemagglutinin antibody confirms expression of the HT-MED1 construct in transfected HEK-293 cells (Lower). Lysis buffers contained 0.5% Nonidet P-40 (lanes 1–4), 0.2% Nonidet P-40 (lanes 5 and 6), or 1% Triton X-100 (lanes 7 and 8).