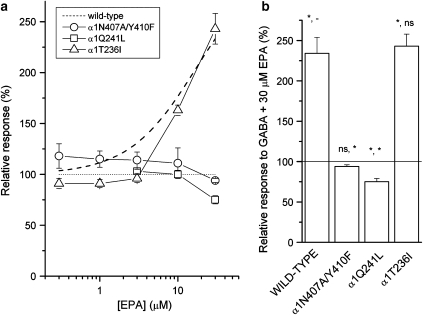
Figure 4.
The effects of mutations to the putative neurosteroid-binding site on channel modulation by eupalmerin acetate (EPA). (a) Modulation by EPA was tested in the presence of an EC25 concentration of GABA (10 μM for the α1N407A/Y410F double mutant, 20 μM for the α1Q241L receptor and 10 μM for the α1T236I receptor). The dashed line is reproduced from Figure 2 and shows potentiation in the wild-type receptor. The symbols represent mean values±s.e.mean. The findings demonstrate that mutations to the putative neurosteroid-binding site also affect channel potentiation by the cembranoid EPA. (b) The relative response to EC25 concentration of GABA+30 μM EPA. The columns show mean values±s.e.mean from three to six cells per construct. Statistical tests were carried out with respect to control (GABA alone) and to EPA-mediated potentiation of the wild-type receptor. *P<0.05; NS, not significant; –, not applicable.