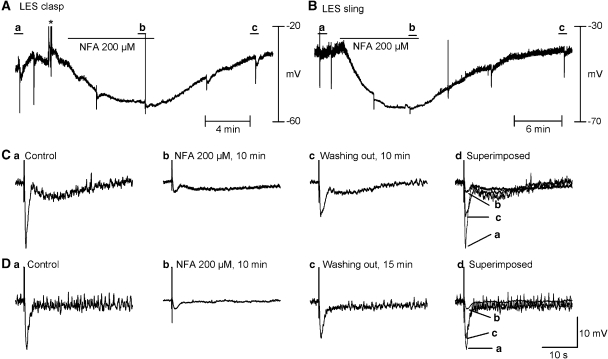
Figure 8.
Niflumic acid (NFA, 200 μM), a ClCa channel blocker, inhibited IJPs induced by nitrergic neurons in the presence of atropine and apamin. (A and B) Continuous recording of membrane electrical activity in clasp and sling muscle for up to 25 min. (C(a–c) and D(a–c)) IJPs before, 10 min after application of NFA and 10 min after wash out in clasp and sling muscles, respectively The effects of NFA were reversible. NFA almost completely abolished membrane potential fluctuations and the apamin-resistant component in both the clasp and sling muscles. The concentration of NFA used was previously found by us to maximally inhibit the nitrergic IJP in opossum LES. *Denotes artifacts resulting from perfusion bubbles. IJP, inhibitory junction potential; LES, lower oesophageal sphincter.