Table 1.
Pharmacology of PGF2α-amides
| PGF2α C1-substituent |
Feline iris |
Swiss 3T3 cell |
Rabbit jugular vein |
Guinea-pig ileum |
Guinea-pig vas deference |
Human platelets (aggregation) |
Human platelets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| •Prostamide | •FP | •FP •EP4 •DP1 | •EP1 | •EP3 | •TP | •DP1, •IP | |
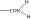 |
21 | 18 000 | 643 | NA | 794 | >10 000 | — |
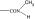 |
28 | 13 300 | — | — | — | — | — |
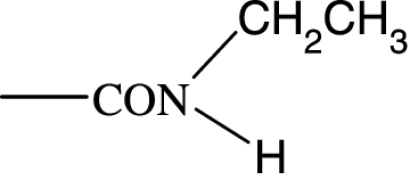 |
35 | — | 250 | >10 000 | >10 000 | — | — |
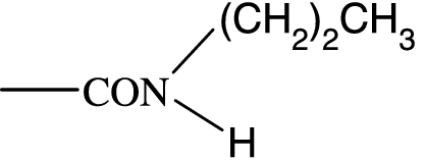 |
19 | — | 281 | NA | >10 000 | — | — |
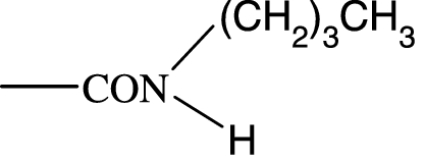 |
60 | — | 17 800 | NA | >10 000 | — | NA |
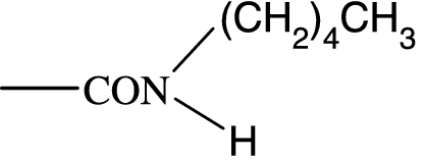 |
158 | — | 17 800 | NA | >10 000 | — | NA |
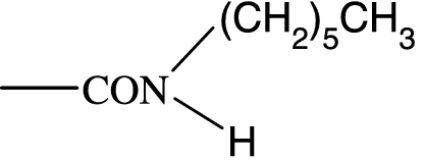 |
258 | — | 20 734 | — | — | — | — |
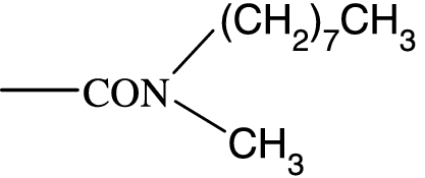 |
771 | — | 3649 | — | — | — | — |
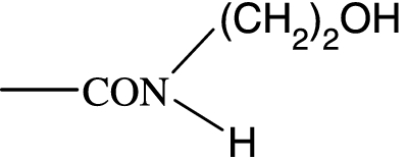 |
57 | 4285 | 1277 | >10 000 | 1590 | NA | NA |
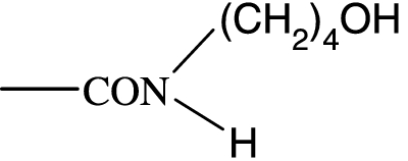 |
158 | — | 2860 | — | — | — | — |
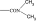 |
4500 | >10 000 | 3649 | — | — | — | — |
Abbreviations: NA, not active; prostamide, prostaglandin-ethanolamide.
Values are EC50 (nM). Experiments involved at least four replicates. Receptor subtype involvement is given (•) under the description of each preparation. Physiological responses are as follows: feline iris=contraction; Swiss 3T3 cells=Ca2+ ↑; rabbit jugular vein=relaxation; guinea-pig ileum=contraction; guinea pig vas deferens=inhibition of field stimulated contraction; human platelets (TP)=aggregation; human platelets (DP, IP)=inhibition of ADP induced aggregation.
