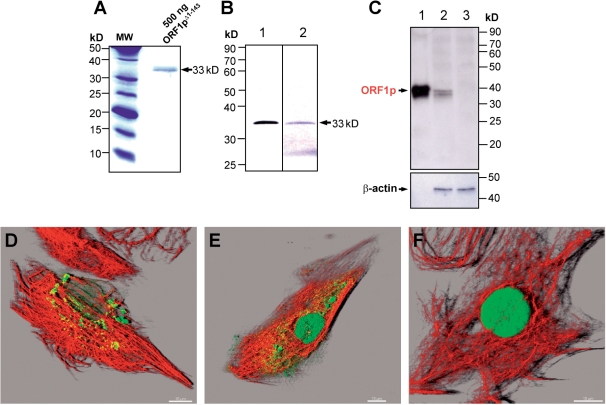
Figure 5.
Monoclonal anti-ORF1pΔ1–143 antibodies (rG24) specifically recognize ORF1-encoded proteins. (A) Recombinant 33-kDa ORF1pΔ1–143 was used for the generation of monoclonal antibodies. MW, molecular weight marker. (B) Immunoblot detection of 10 ng of purified His-tagged ORF1pΔ1–143 with rG24 (lane 1) and anti-His-tag antibodies (lane 2). (C) Immunoblot analysis examining the specificity of the generated monoclonal anti-ORF1p antibody. Sixty microgram whole cell extracts from pORF1pΔ1–143-IRESpuro (lane 2)- or pIRESpuro-transfected (lane 3) REF cells were loaded on a 12% SDS–PAA gel. In contrast to the parental empty expression vector pIRESpuro, pORF1pΔ1–143-IRESpuro is expressing the N-terminally truncated 33-kDa L1Rn-ORF1 protein, which is detected by the rG24 antibody. As a loading control the membrane was stripped and incubated with an anti-β-actin antibody; lane 1, 10 ng purified ORF1pΔ1–143 protein; (D–F) Confocal images of REF cells transfected with ORF1p- (D, E) and ORF1pΔ1–143- (F) expressing constructs. ORF1-encoded proteins and vimentin were stained using monoclonal rG24 (green) and polyclonal anti-vimentin antibodies (red), respectively. The co-localization channel (yellow) was generated using the ImarisColoc module. Cytoplasmic ORF1p aggregates co-localize with vimentin filaments partially. Scale bar—10 µm.