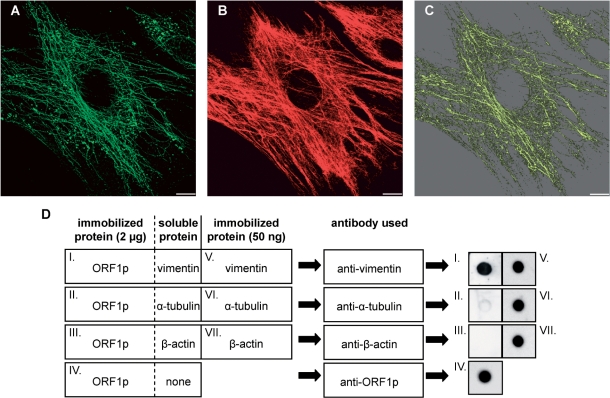
Figure 6.
L1Rn ORF1p is able to form filaments that co-align with vimentin filaments. (A and B) In situ overlay of recombinant L1-21 ORF1p onto PFA-fixed and Triton X-100-extracted MEFs. Immunofluorescence images of L1Rn ORF1p (A) and vimentin (B) are shown in green and red colors, respectively. Each panel represents the 3D reconstruction of xy confocal sections. (C) ORF1p and vimentin filaments co-align partially. The co-localization channel (yellow) was generated using the ImarisColoc module. Scale bar—10 µm. (D) Dot blot overlay assay demonstrating interaction of ORF1p with vimentin. ORF1p was immobilized onto a nitrocellulose membrane (dots I–IV). Each ORF1p dot contained 2 μg of protein. After blocking, immobilized ORF1p was overlaid with an excess of soluble vimentin, α-tubulin or β-actin, respectively. Incubation was carried out for 60 min. In order to control for successful immobilization and immunoblotting procedure, 50 ng of soluble vimentin, α-tubulin and β-actin were immobilized on the nitrocellulose membrane in parallel (dots V–VII). Membranes were washed subsequently and submitted to immunoblot analyses with anti-vimentin, anti-α-tubulin or anti-β-actin antibodies, respectively, due to the schematic shown. In contrast to α-tubulin and β-actin, only vimentin can be detected with its specific antibody on the nitrocellulose membrane, after overlaying ORF1p dots with the respective IF protein (dots I–III). This is indicating that only vimentin is binding to ORF1p.