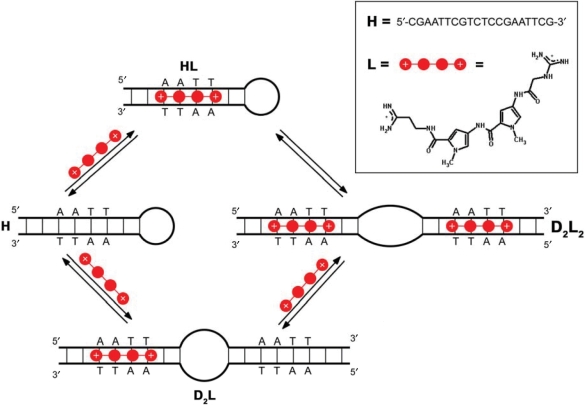
Figure 1.
Mechanism of binding of the minor groove-directed ligand to the DNA oligonucleotide. The proposed mechanism that is well supported by experimental data (Figure 4) shows that the binding-coupled conformational changes are crucial for interpretation of DNA (hairpin=H) association with a classical minor groove binder (netropsin=L). D2L and D2L2 represent the duplex conformations complexed by one or two molecules of L, respectively.