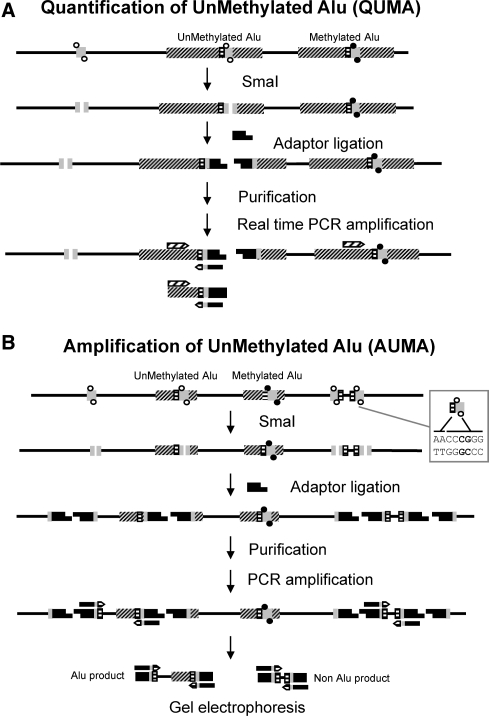
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the QUMA and AUMA methods. DNA is depicted by a solid line, Alu elements are represented by dashed boxes. The QUMA and AUMA recognition sites (AACCCGGG) are represented by dashed/gray boxes. CpGs at SmaI sites are shown as full circles when methylated and as open circles when unmethylated. The methylation-sensitive restriction endonuclease SmaI can only digest unmethylated targets, leaving blunt ends to which adaptors can be ligated. (A) QUMA is performed by real-time PCR of an inner Alu fragment using a primer complementary to the Alu consensus sequence upstream of the SmaI site and the primer complementary to the adaptor to which two Alu homologous nucleotides (TT) have been added. (B) In AUMA, sequences flanked by two ligated adaptors are amplified by PCR using a single primer, the same adaptor primer plus the TT nucleotides. When only a few nucleotides are added to the primer, i.e. TT, as illustrated here, other non-Alu sequences may be amplified. This allows the amplification of a large number of sequences that typically range from 100 to 2000 bp.