Figure 1. Phylogenetic relationship of IGFBP and IGFBP-rP gene products.
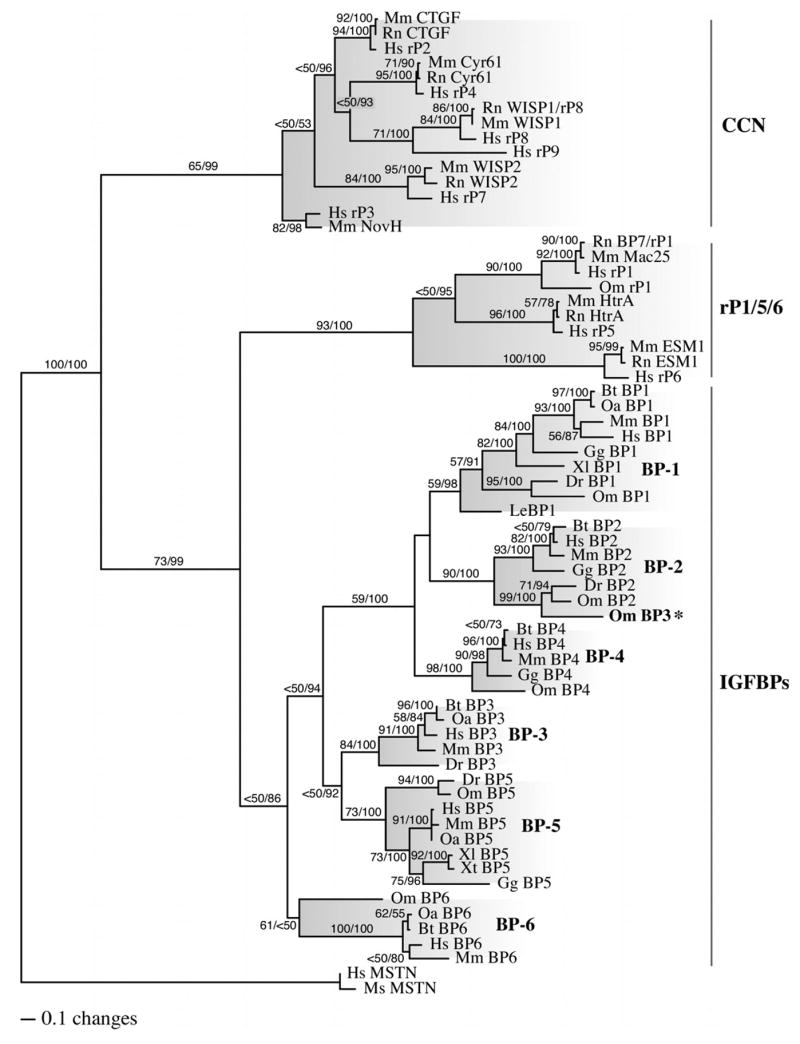
Maximum likelihood (ML), ML boootstrap, and Bayesian inference analyses were performed on a single matrix composed of homologous amino acid sequences from various vertebrate species using PHYLIP 3.66 and MrBayes v.3.0 (Bt, Bos taurus; Dr, Danio rerio; Gg, Gallus gallus; Hs, Homo sapiens; Le, Leucoraja erinacea; Mm, Mus musculus; Ms, Morone saxatilis; Oa, Ovis aries; Om, Oncorhynchus mykiss; Xl, Xenopus laevus; Xt, Xenopus tropicalus). A total of 100 ML bootstrap iterations and 10,000,000 Bayesian generations were performed (trees saved every 100 generations). Trees from the first 2,000,000 generations were discarded as burn-in to assure that stationarity was established and the remaining 80,000 post burn-in trees were used to construct the majority rule consensus tree shown with PAUP*. Two independent analyses were performed and produced identical results. ML bootstrap and Bayesian posterior probability values are shown above each branch (ML/Bay. PP) when greater than 50%. The major subclades are shaded and the monophyletic IGFBP group and the paraphyletic IGFBP-rP groups are labeled on the right. (BP, IGFBP; rP, IGFBP-rP; MSTN, myostatin; CCN proteins include CTGF, Cyr61, WISP, NovH & IGFBP-rP2-4,7-9; IGFBP-rP1,5,6 include Mac25, HtrA & ESM; * misannotated)
