Figure 1.
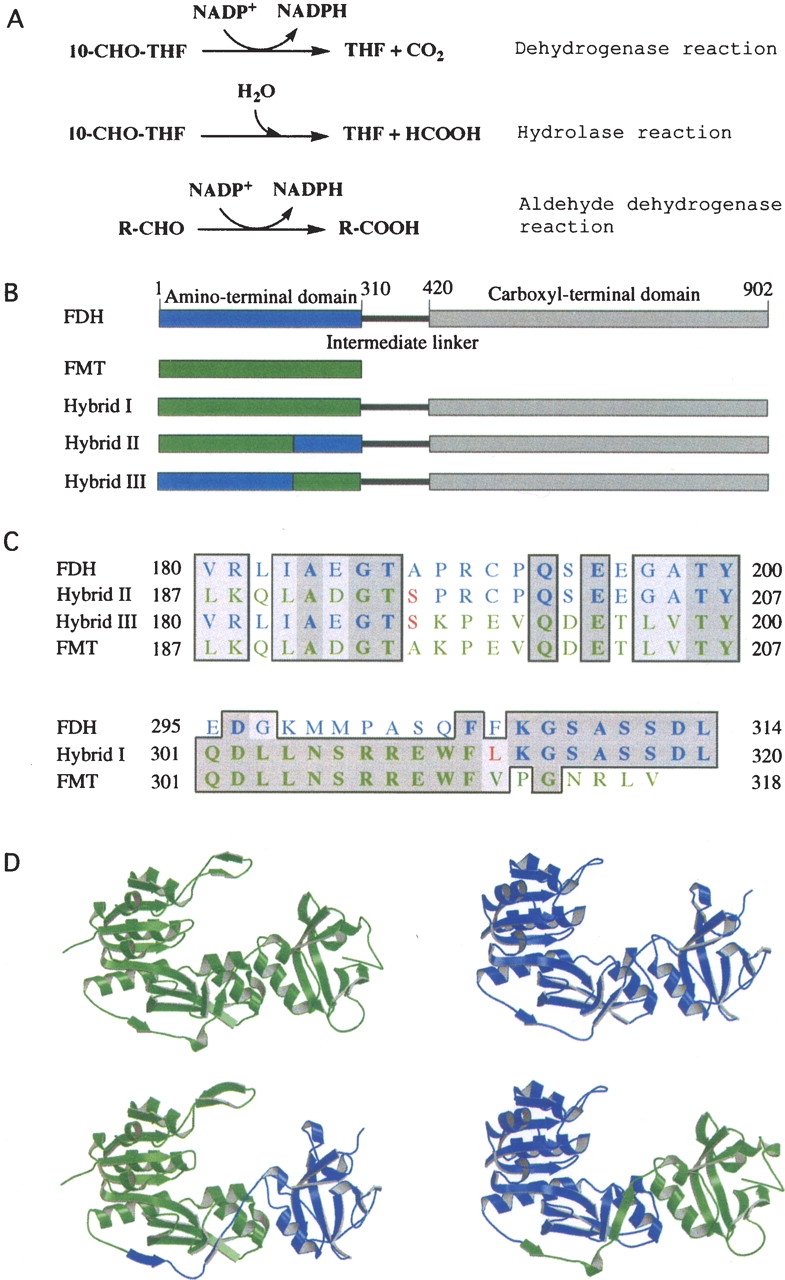
(A) Reactions catalyzed by FDH (the full-length FDH catalyzes all three reactions; the amino-terminal domain catalyzes the hydrolase reaction; the carboxy-terminal domain catalyzes the aldehyde dehydrogenase reaction). (B) Schematic diagram of FDH monomer (blue, the amino-terminal domain; gray, the carboxy-terminal domain; black, the intermediate linker) and FMT/FDH hybrid proteins, showing portions of Nt-FDH (blue) and FMT (green) within each hybrid. (C) Partial sequence alignments of FDH, FMT, and hybrid proteins showing the amino-terminal splice junction (top) and the carboxy-terminal splice junction (bottom). Dark-shaded residues are identical, whereas light-shaded residues are similar. Residues originating from FDH are shown in blue and those from FMT in green. Unique residues created by the insertion of restriction sites are in red. Note that hybrid III has a carboxy-terminal splice junction identical to that of hybrid I. The alignment was prepared using MacVector. (D) Ribbon presentation of crystal structures of FMT (upper left) (PDB ID 2FMT) and Nt-FDH (upper right) (PDB ID 1S3I) along with models of the Nt-FDH homologous region of hybrid II (lower left) and hybrid III (lower right). Hybrid models were prepared using SYBYL 7.0. FMT and Nt-FDH structures were superimposed, and relevant portions of each protein were merged together in a separate area. Hybrid structures were generated by creating bonds between the chains. The resulting hybrid structures were energy-minimized. Visual depictions were generated using MOLSCRIPT (Kraulis 1991).
