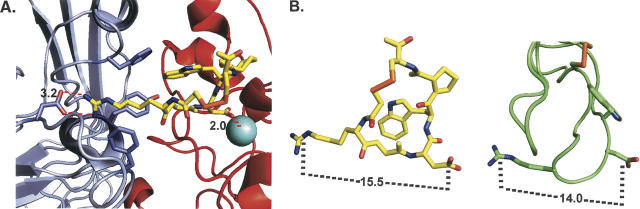
Figure 7.
Modeling eptifibatide/echistatin:αIIbβ3 interactions. (A) This figure is based on the crystallographically determined structure of the eptifibatide:αIIbβ3 ectodomain complex, 1TY6.pdb (Xiao et al. 2004). The αIIb subunit is shown in light blue, the β3 subunit in red, and eptifibatide in yellow with its functional groups colored as follows: nitrogen, blue; oxygen, red; sulfur, orange. Selected αIIb residues that interact with eptifibatide are highlighted including Asp 224, located 3.2 Å distant from the ligand's positively charged guanidinium moiety, and Phe 160, Tyr 190, and Phe 231, which pack around the homoarginine's aliphatic segment. Likewise, eptifibatide aspartate, which interacts with the β3 subunit's MIDAS Mg++ cation (2.0 Å away), is emphasized. (B) This figure compares the structures of eptifibatide (as in panel A) and echistatin, based on the NMR determined structure, 1R03.pdb (Monleon et al. 2005). The distances between key electrostatic residues on each ligand, eptifbatide's homoarginine (Cζ) and its aspartate (Cδ), echistatin's Arg 24 (Cζ) and Asp 26 (Cδ), are indicated by dashed lines. Echistatin's polypeptide backbone is shown as a green tube with selected residues highlighted.