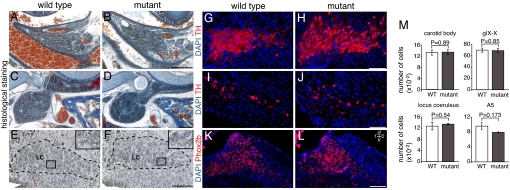
Fig. 4.
Analysis of structures that depend on Phox2b for proper development and are involved in respiratory control in Phox2b27Ala/+ and Phox2b+/+ neonates. (A–D) The CB is preserved in newborn mutants (A and B), as is the petrosal/nodose (gIX/X) ganglionic complex (C and D). (E–H) The LC appears normal by histology (E and F) and TH immunohistochemistry (G and H) in the mutants. In E and F, the LC is encircled by a dashed line. (Insets) Enlargements of the framed areas showing the typical large LC neurons that were counted. (I and J) The noradrenergic neurons of the A5 cell group are detected in similar numbers by TH immunohistochemistry in wild-type and mutant neonates. (K and L) As assessed by Phox2b immunohistochemistry, the nTS is not detectably altered in Phox2b27Ala/+ mutants. Sagittal sections are shown (Scale bars: B, D, F, H, and J, 0.1 mm; L, 0.2 mm.) (M) Counts of glomus cells in the CB, of gIX/X and LC neurons, and of A5 cells. The estimated cell number per animal is given (mean ± SEM for three pups of each genotype).