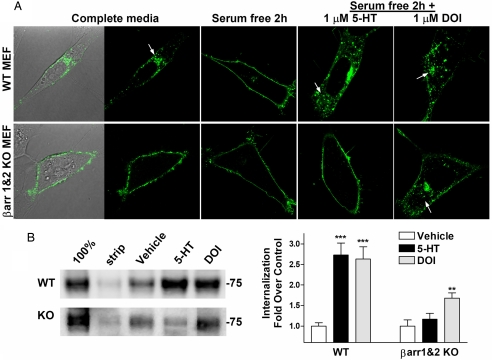
Fig. 3.
Agonist-induced internalization of 5-HT2AR-YFP expressed in WT and β-arrestin-1- and β-arrestin-2-KO MEFs. (A) (Upper) WT cells incubated in complete media have mostly internalized 5-HT2AR-YFP (Left, DIC light image to show cell body outline). Serum removal (serum-free for 2 h) returns receptors to cell surface. (Lower) The 5-HT2AR-YFP is on the cell surface of β-arrestin-1- and β-arrestin-2-KO (βarr1&2-KO) MEFs regardless of serum content. Addition of 1 μM serotonin (5-HT) for 30 min internalizes the 5-HT2AR-YFP in WT, but not βarr1&2-KO MEFs. DOI (1 μM, 30 min) internalizes 5-HT2AR-YFP in both cell types. (B) Internalization of HA-5-HT2AR as determined by cell surface biotinylation assay. Cell surface proteins were biotinylated; cells were then treated with 1 μM drug or vehicle for 1 h. (Left) In the representative 5-HT2AR immunoblot, 100% represents surface biotinylation without glutathione stripping, and strip represents cells that were treated with glutathione yet did not undergo vehicle or drug treatment incubation. The 75-kDa molecular weight marker is indicated. (Right) Densitometric analysis of multiple experiments is presented with statistical analysis. One-way ANOVA was performed on each genotype for drug effect, followed by Bonferroni post hoc analysis. WT: treated vs. vehicle, ***, P < 0.001; βarr1&2-KO: treated vs. vehicle, **, P < 0.01. WT plus DOI vs. βarr1&2-KO plus DOI did not significantly differ (P > 0.05; n = 9–10 WT treatments in five separate experiments; n = 4–8 KO in three separate experiments).