Figure 1.
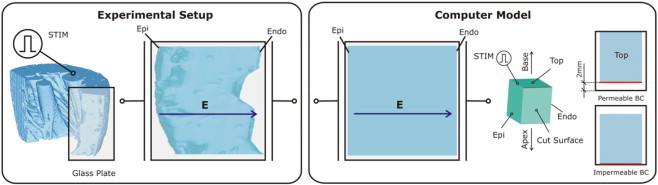
Schematics of the experimental setup in the studies by Fast and co-workers (10–12) and of the computer model. In both model and experiment, the wedge preparation was paced via an electrode located at the preparation edge (STIM). Rectangular shocks were delivered via two large mesh electrodes located at opposite borders of the tissue-bath chamber. The direction of the applied electric field E is indicated by the arrows. The wedge model is of dimensions 1.2 × 1.2 cm of the endo- and epicardial surfaces, and a transmural thickness of 1 cm. The computer model panel also presents a schematic of how permeable and impermeable boundary conditions were implemented on the cut surface of the wedge in accordance with the experimental procedure.
