Table 2. Data-collection statistics for heavy-atom derivatives.
Values in parentheses are for the highest resolution shell.
| K2PtCl4 derivative | HgCl2 derivative | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.0718 | 1.0722 | 1.009 | 1.0092 |
| Resolution range (Å) | 33.15–2.0 (2.1–2.0) | 33.33–2.0 (2.1–2.0) | 38.1–2.3 (2.4–2.3) | 36.6–2.3 (2.4–2.3) |
| Unique reflections | 51441 | 51635 | 33651 | 33504 |
| Rsym† (%) | 7.3 (38.9) | 7.3 (38.9) | 9.0 (36.4) | 9.0 (36.5) |
| Completeness (%) | 95.5 (75.1) | 95.5 (74.8) | 98.4 (97.3) | 98.4 (97.3) |
| Anomalous completeness (%) | 91.8 (63.9) | 92.1 (74.8) | 97.1 (87.7) | 96.9 (87.4) |
| 〈I/σ(I)〉 | 17.3 (2.8) | 17.4 (2.8) | 25.6 (8.1) | 24.9 (8.0) |
| Mosaicity (°) | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.34 | 0.34 |
| Total observations | 325071 | 330711 | 419416 | 408115 |
| Multiplicity | 6.3 | 6.3 | 12.5 | 12.5 |
| Anomalous multiplicity | 3.4 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 6.7 |
| MAD phasing statistics | ||||
| Phasing power‡ | ||||
| Isomorphous | — | 0.543 | — | 0.338 |
| Anomalous | 2.094 | 1.267 | 1.010 | 0.867 |
| Overall figure of merit | 0.4811 | 0.3930 | ||
| Rcullis | ||||
| Isomorphous | — | 0.683 | — | 0.840 |
| Anomalous | 0.726 | 0.739 | 0.883 | 0.901 |
R
sym = 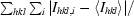
 .
.
Phasing power is FHc/E for the isomorphous case and 2 FH /E for the anomalous case, where FHc is the calculated heavy-atom structure factor and E is the r.m.s. lack of closure.
/E for the anomalous case, where FHc is the calculated heavy-atom structure factor and E is the r.m.s. lack of closure.
