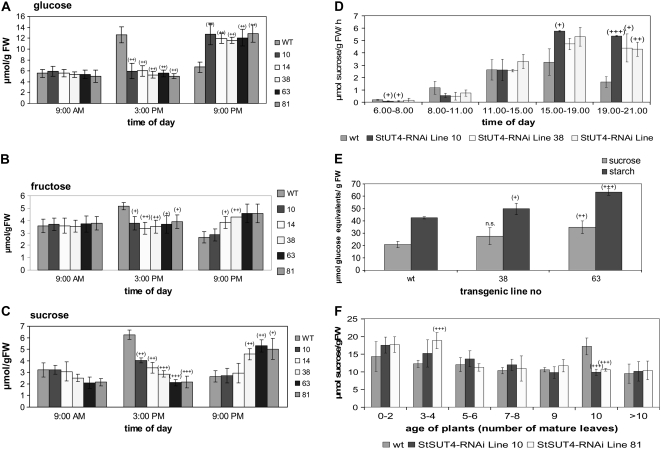
Figure 6.
A to C, Content of soluble sugars in source leaves of StSUT4-RNAi plants compared to potato wild-type plants determined enzymatically. At the end of the light period, transgenic plants show significantly increased Glc (A), Fru (B), and Suc (C) content per gram fresh weight. D, Efflux of Suc from leaves of wild-type and StSUT4-RNAi plants was determined by exudation in the presence of EDTA. Suc exudation was determined enzymatically in intervals of 3 h during the light period from plants kept under LD conditions in the greenhouse. Suc efflux from wild-type leaves shows maxima at the end of the light period, whereas in StSUT4-RNAi plants Suc efflux remains high even in darkness. E, Suc and starch content of in vitro-grown microtubers (n = 4 for each plant line). Tubers were harvested 20 d after tuber induction in darkness. sd is given. F, Suc content in the shoot apical meristem of potato wild-type and StSUT4-RNAi plants. Samples were taken at the end of the light period (9 pm). Fresh weight of samples was between 20 and 60 mg. Error bars indicate sd. Experiments were performed under LD conditions. Note that floral buds of StSUT4-RNAi plants were first detected when plants had five to six mature leaves, whereas wild-type potato plants started transition from the vegetative to the generative phase when they had >10 leaves.