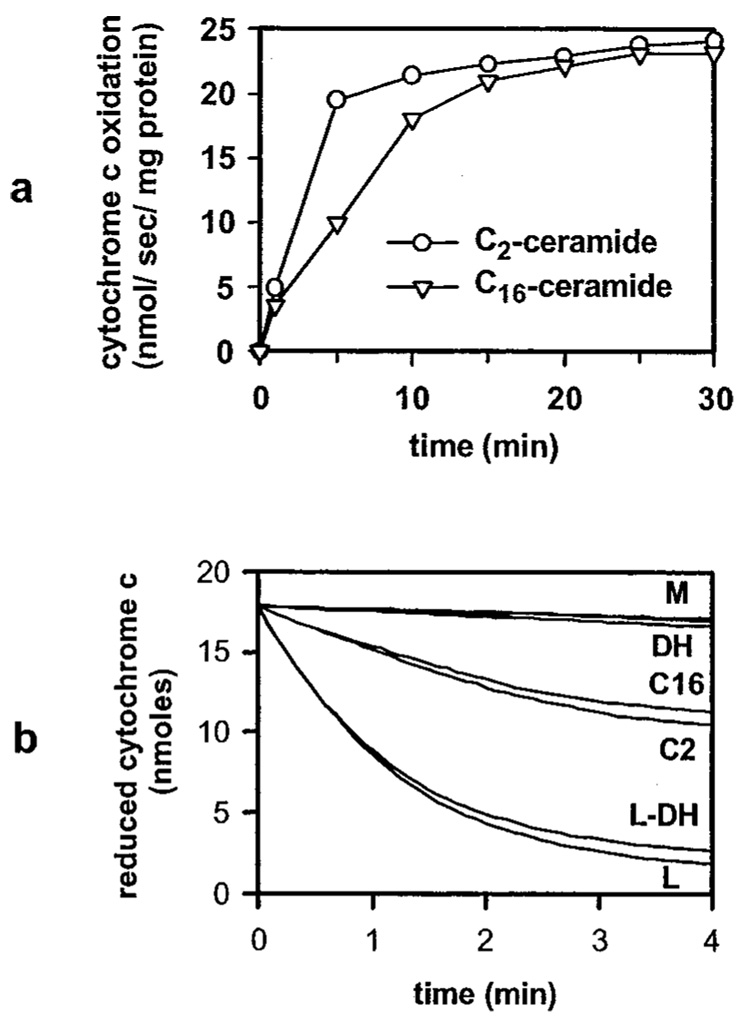
FIG. 2. C2- and C16-ceramide increase the permeability of the mitochondrial outer membrane to cytochrome c in a dose- and time-dependent manner.
Mitochondria were incubated for the indicated time periods and with the indicated concentrations of C2- (circles) or C16-ceramide (triangles) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Reduced cytochrome c was then added and the absorbance was monitored at 550 nm. The initial rates plotted were in nanomoles of cytochrome c oxidized per s/mg of mitochondrial protein. Results are representative experiment of at least 3 performed on separate mitochondrial preparations. a mitochondria incubated for the indicated time periods with 20 µm ceramides. b, mitochondria incubated with the following treatments: mitochondrial controls (M; untreated mitochondria, vehicle controls, 83 µm BSA for 15 min, with overlapping lines); 20 µm C2-dihydroceramide for 10 min (DH); 20 µm C2-ceramide for 10 min (C2); 20 µm C16-ceramide for 10 min (C16); lysed mitochondria were incubated for 10 min with 20 µm C2-dihydroceramide (L-DH); lysed mitochondrial controls (L; untreated lysed mitochondria, lysed mitochondria incubated for 10 min with 20 µm C2-ceramide, C16-ceramide, or vehicles or 15 min with 83 µm BSA, with overlapping lines).