Figure 1. Direct interaction of insulin signaling and inflammatory pathways.
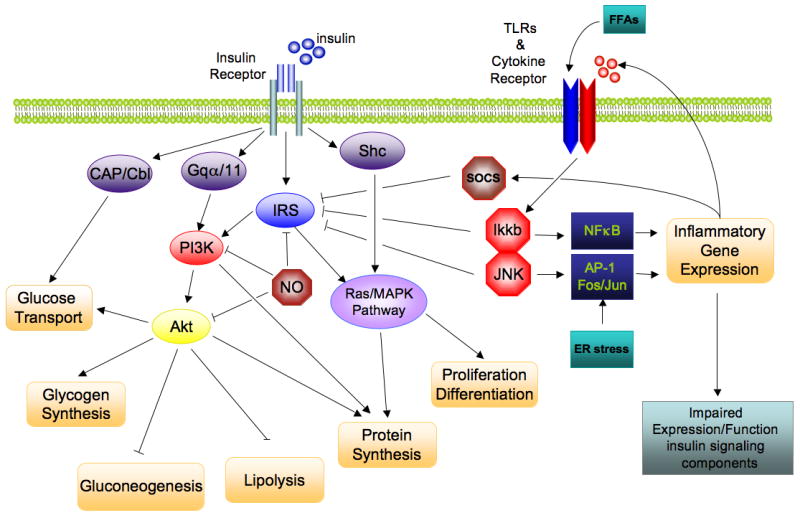
The insulin signaling cascade branches into two main pathways. The PI3K/AKT pathway mediates insulin action on nutrient metabolism including glucose uptake. The Ras/MAPK pathway mediates insulin’s effect on gene expression, but also interacts with the PI3K-AKT pathway to control cell growth and differentiation. Activation of the insulin receptor leads to tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS1 thereby initiating signal transduction. Stimulation of the NFκB and AP-1 Fos/Jun inflammatory pathways results in the activation of the serine kinases, Ikkb and Jnk1, which reduce the signaling ability of IRS1. Additional inflammation-related negative regulators of IRS proteins include the Socs proteins and NO, which are induced in inflammation, and promote IRS degradation. NO also reduces PI3K/Akt activity by s-nitrosylation of Akt.
