Figure 2. Obesity and the development of inflammation and insulin resistance.
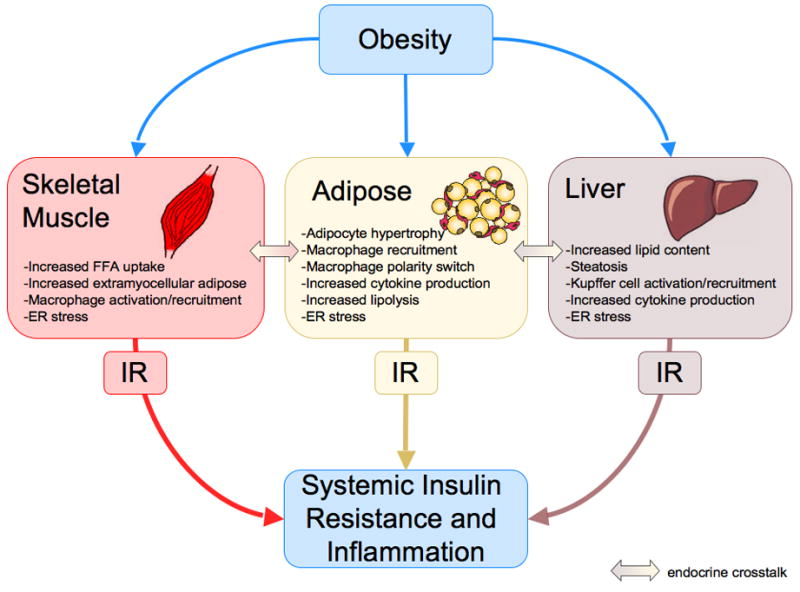
Obesity-induced changes in skeletal muscle, adipose tissue and the liver result in localized inflammation and insulin resistance (IR) through autocrine and paracrine signaling. Endocrine-mediated cross-talk between insulin target tissues contributes to insulin resistance in distant tissues. Systemic inflammation and insulin resistance are the net effect of these changes.
