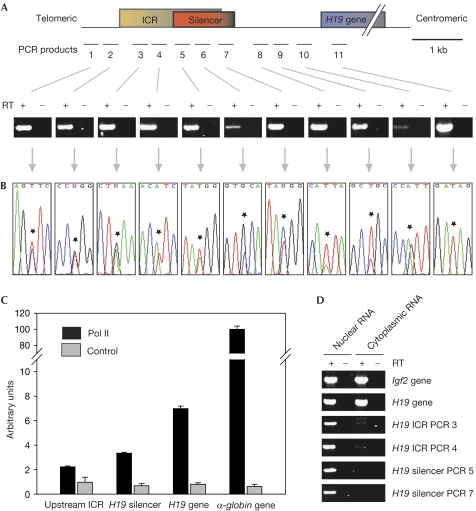
Figure 1.
The mouse H19 upstream regulatory region is biallelically transcribed. (A) Schematic representation of the mouse H19 locus and the PCR amplicons used in reverse transcription reactions. The imprinting control region (ICR) extends from −4 to −2 kb in relation to the H19 gene transcription start site, overlapping with the silencer (−2.9 to −1.7 kb relative to the H19 transcription start site). PCR products shown below were amplified from complementary DNA obtained from an F1 generation fetal liver (embryonic day (E)15.5) of a C57Bl6/SD7 cross using random primers, with or without reverse transcriptase (RT). (B) Selected sequence traces of PCR products shown in (A). Asterisks indicate SNPs between the C57Bl6 and SD7 strains. (C) Pol II occupancy at the H19 region. Real-time PCR of ChIP material obtained with an antibody against Pol II or a control antibody. Sequences correspond to amplicons 2 (upstream ICR), 5 (H19 silencer) and 11 (H19 gene), and a control fragment from the α-globin gene. (D) Analysis of the subcellular localization of the ICR transcripts. RNA from mouse embryonic fibroblasts was fractionated and reverse transcription reactions were carried out on the nuclear and the cytoplasmic RNA pools, respectively. ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; Pol II, RNA polymerase II; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism.