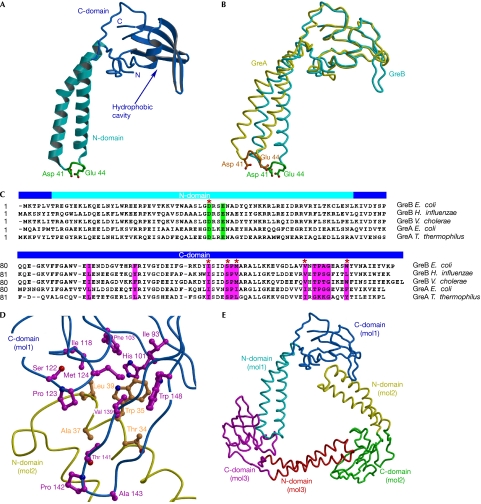
Figure 1.
Structure of the GreB protein. (A) Overall structure. The α-helical turn at the tip of the N-domain and the two principal acidic side chains are shown in green. (B) Structures of GreB and GreA superimposed by the C-domains. (C) Sequence alignment of the Gre factors. The principal acidic residues and the conserved hydrophobic residues lining the C-domain cavity are highlighted in green and magenta, respectively. We included serine and threonine, whose small polar side chains often appear in the hydrophobic cores of proteins, as residues that contribute to the hydrophobic intermolecular interface, as observed in the GreB trimers (D). GreB residues that were altered in the present study are marked by red asterisks. (D) Hydrophobic interface formed between two GreB molecules in the asymmetric unit. (E) Overall view of the trimer that the GreB monomers form in the crystal. C-domain, carboxy-terminal domain; N-domain, amino-terminal domain.