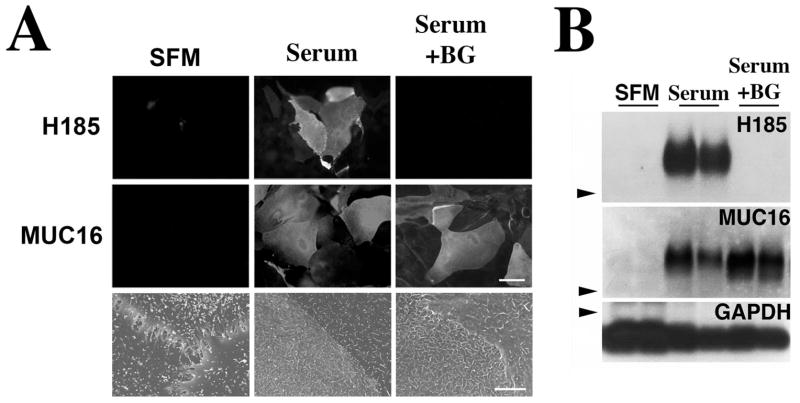
Figure 1.
Alteration of mucin O-glycosylation in HCLE cells treated with benzyl-α-GalNAc. Addition of serum to HCLE cell cultures triggered the biosynthesis of cell surface-associated MUC16 and its H185 carbohydrate epitope, as determined by immunofluorescence (A) and Western blot (B), as well as the appearance of microplicae at the cell surface, as determined by scanning electron microscopy. In the presence of benzyl-α-GalNAc, HCLE cells did not synthesize the MUC16-associated H185 carbohydrate epitope. The inhibitor did not affect either the biosynthesis of MUC16 or the cell surface ultrastructural features of HCLE cells compared with serum treatment alone. Arrowheads: position of the 250-kDa molecular weight marker in the agarose gel. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Scale bars: 60 μm (immunofluorescence images), 5 μm (scanning electron microscopy images).