Figure 2.
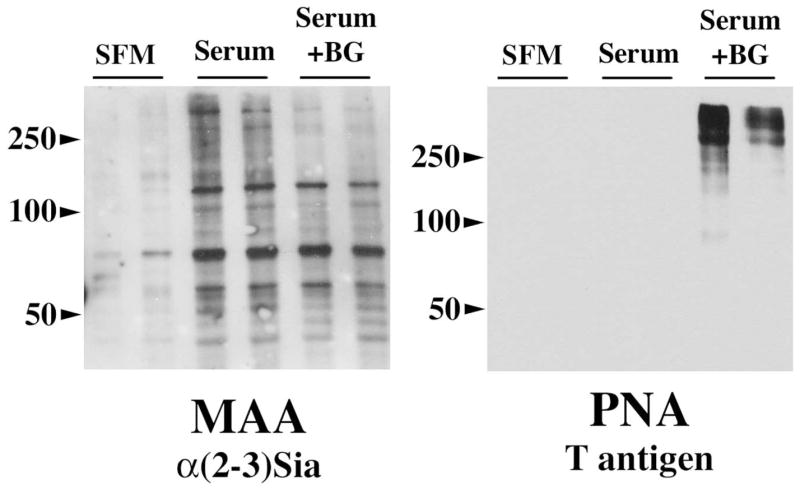
Effect of benzyl-α-GalNAc on biotinylated cell surface glycoproteins in HCLE cells. As determined by MAA binding, benzyl-α-GalNAc decreased O-linked sialylation on high molecular weight glycoproteins, which correlates with decreased binding of the H185 antibody to the cell surface–associated mucin MUC16 after benzyl-α-GalNAc treatment (Fig. 1). Binding of PNA to the mucin-associated T-antigen increased after benzyl-α-GalNAc treatment, most likely as a consequence of the reduced levels of terminal sialic acid on the cell surface mucins. Experiments were performed in duplicate.
