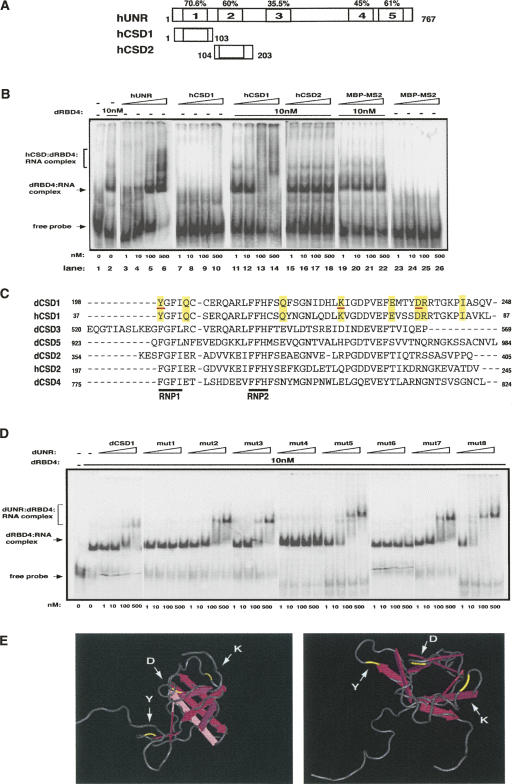
FIGURE 2.
Residues of dCSD1 involved in SXL and msl-2 interactions. (A) Schematic representation of hUNR and its fragments. The positions of the first and last amino acids of each construct as well as the conservation of each CSD are indicated. (B) The CSD1 of hUNR interacts with SXL. Recombinant proteins were expressed as His-tagged fusions and tested as indicated in the legend of Figure 1. hCSD1 and hCSD2 also contained a MS2-tag. MBP-MS2 was included as a negative control. The positions of the different complexes are indicated. (C) Alignment of CSDs of Drosophila and human UNR. The indicated CSDs were aligned using ClustalW (EBI). The RNP motifs (RNP1 and RNP2) are underlined in black. The amino acids common for dCSD1 and hCSD1, but different for the rest of the CSDs are shadowed in yellow. The amino acids interacting with SXL and msl-2 are underlined in red (see below). (D) Binding of single-point dCSD1 mutants to msl-2. The amino acids shadowed in yellow in C were named 1–8 and were mutated to alanine. Mutant proteins were expressed as MBP fusions and used for EMSA as described in the legend of Figure 1. (E) Stereo-view of hCSD1 showing the position of relevant amino acids. Five anti-parallel β-strands (pink arrows) give an overall β-barrel fold. The SXL and msl-2 interacting residues are depicted in yellow.