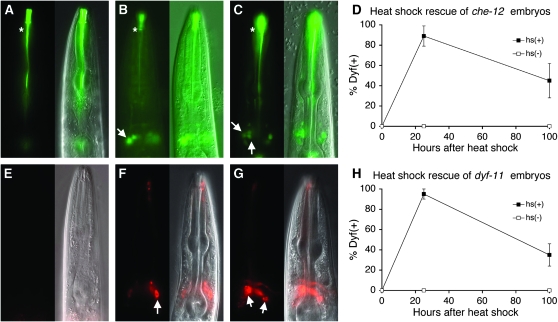
Figure 6.—
CHE-12 and DYF-11 act cell-autonomously and are required continuously for cilium morphology and function. (A) che-12(mn389) animals fail to take up FITC; asterisk indicates nonspecific staining. Fourth larval stage (L4) animals are depicted in all images. (B) Expression of CHE-12 in a che-12(mn389) mutant animal within only two amphid neurons, ASH and ASI, using the sra-6 promoter, rescues the Dyf defect only within these neurons (arrow). (C) A che-12(mn389) animal that is provided CHE-12 via heat shock as an adult is able to take up FITC in several amphid neurons (arrows). (D) che-12(mn389) embryos carrying extrachromosomal arrays containing the hsp-16.2 pro∷che-12 cDNA transgene were heat-shocked for 30 min at 34°. Dye filling was performed after 24 hr to determine initial rescue or after 100 hr. (E) dyf-11 animals cannot take up DiI. (F) Expression of dyf-11 in ASH and ASI using the sra-6 promoter enables only these two neurons to fill with dye (arrow). (G) Providing DYF-11 to adult animals via heat shock rescues their Dyf defect. Animals contain an hsp-16.2 pro∷dyf-11 cDNA transgene. (H) Same as D, except that dyf-11(mn392) mutants carrying an hsp-16.2 pro∷dyf-11 transgene were used.