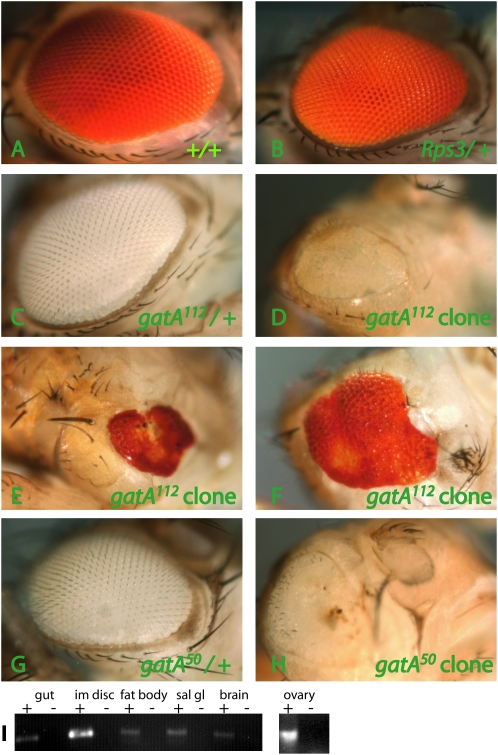
Figure 6.—
Mosaic analysis and expression of gatA. w, ey-FLP, Gla-lacZ; FRT Rps3, P{ubi-GFP, w+}/TM6B females were crossed with FRT e gatA50/TM3, Sb males, FRT e gatA112/TM3, Sb males or FRT +/TM3, Sb males. (A–H) Adult eyes. The FRT Rps3 chromosome carries a w+ transgene. Rps3 is recessive cell lethal. Therefore, in males, cells that have not undergone recombination are yellow. Cells that have recombined are white (homozygous for + or gatA, depending on the cross). (A, B, E, and F) Female eyes are w+, aiding phenotypic analysis, but making it difficult to determine the genotype of cells. (C, D, G, and H) Male eyes are w−, permitting easy genotyping of eye clones. (A) Wild-type clone shows normal growth and development. (B) Rps3/+ eyes (no clones induced) are slightly smaller than wild type. (C) gatA112/+ eyes (no clones induced) and (G) gatA50/+ eyes (no clones induced) are normal. (D–F) gatA112 clones and (H) gatA50 clones cause small, misshapen eyes with cuticle scars and ectopic bristles. There is a small, pale yellow region in the top portion of the eye in D, because ey-FLP induced mitotic recombination somewhat late in this eye. (I) RT–PCR of gatA from RNA extracts from larval gut (lanes 1 and 2), imaginal discs (lanes 3 and 4), fat bodies (lanes 5 and 6), salivary gland (lanes 7 and 8), brain (lanes 9 and 10), and from adult ovary (separate gel, lanes 11 and 12). “+” and “−” refer to treatment of extracts with reverse transcriptase.