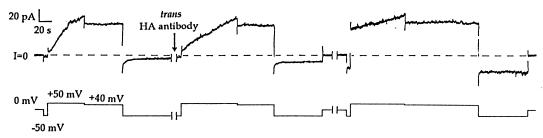
Figure 2.
The effect of trans anti-HA on HA-inserted colicin Ia. The upper trace is membrane current, and the lower trace is the voltage of the cis compartment with respect to the trans. Several minutes before the start of the record, 0.8 μg of HA-inserted colicin Ia (mutant HA-III) (plus 10 μg octyl glucoside) was added to the cis compartment, and the membrane was pulsed between positive and negative voltages to check for normal voltage gating. (For mutant HA-III, a small component of the conductance turned off slowly at −50 mV. This is seen as the small residual conductance at −50 mV, which has not yet gone to zero before the first break.) During the first break in the record (1 min), 20 μg of anti-HA was added to the trans compartment. The voltage was pulsed to +50 mV to turn on the conductance and then held at +40 mV to give the open colicin channels a longer exposure to trans antibody. Upon stepping to −50 mV, the turn-off of the conductance showed substantial inhibition. After several more voltage pulses during the second break (10 min), an even greater fraction of the conductance failed to turn off. A subsequent pulse to +50 mV and then to +40 mV resulted in a further increase in this fraction. Thus, the effect of trans anti-HA is to prevent open channels from closing, presumably because of the binding of antibody to the translocated HA epitope in the mutant colicin. The solutions on both sides of the membrane were 100 mM KCl/5 mM CaCl2/1 mM EDTA/20 mM Hepes, pH 7.2. The recording was taken from a chart record filtered at 100 Hz.