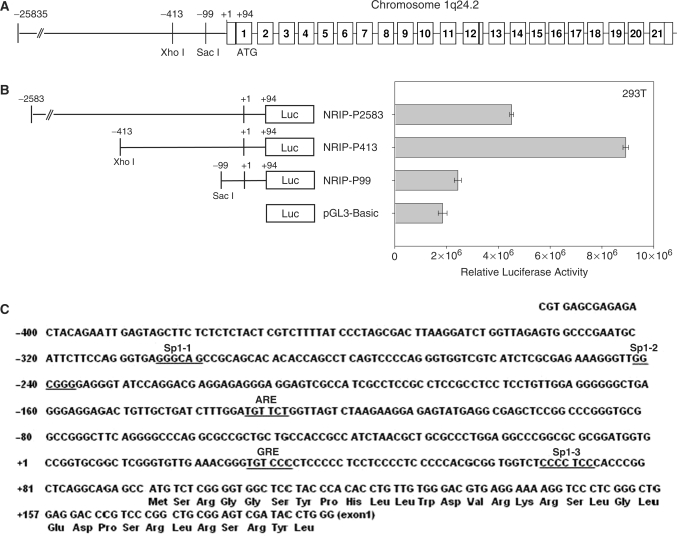
Figure 1.
Identification of the promoter region in the NRIP gene. (A) Genomic organization of the human NRIP gene on chromosome 1q24.2. The numbers in box refer to exon regions. (B) Identification of the promoter activity in the 5′-flanking region of the NRIP gene. The nucleotides between –2583 and +94 relative to the transcription start site of the NRIP gene were amplified by PCR and cloned into pGL3-Basic and then named NRIP-P2583. Series deletions of ∼ −413 to +94 and ∼ −99 to +94 regions were constructed by XhoI and SacI digestion and cloned into pGL3-Basic and named NRIP-P413 and NRIP-P99, respectively. 293T cells were transiently co-transfected into the indicated reporter promoter with pRL-CMV (as an internal control). The relative luciferase activity is expressed as the measured firefly luciferase activities (promoter activity), which were normalized by renila luciferase activity (pRL-CMV). The results are shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (C) The putative transcription factor binding elements in the NRIP gene. The NRIP promoter sequences (–413 to +94) were analyzed by Transcription Element Search System (TESS, http://www.cbil.upenn.edu/cgi-bin/tess/tess). Three Sp1 and two hormone response elements, ARE and GRE, were underlined.