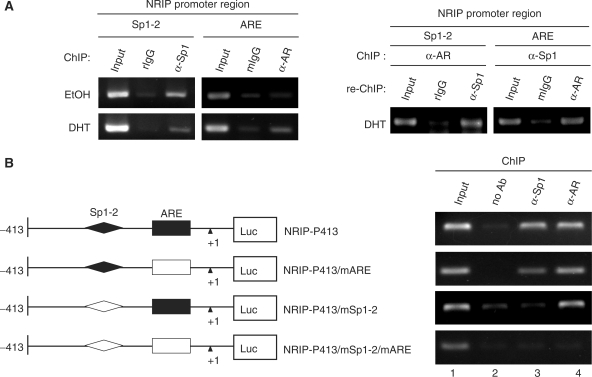
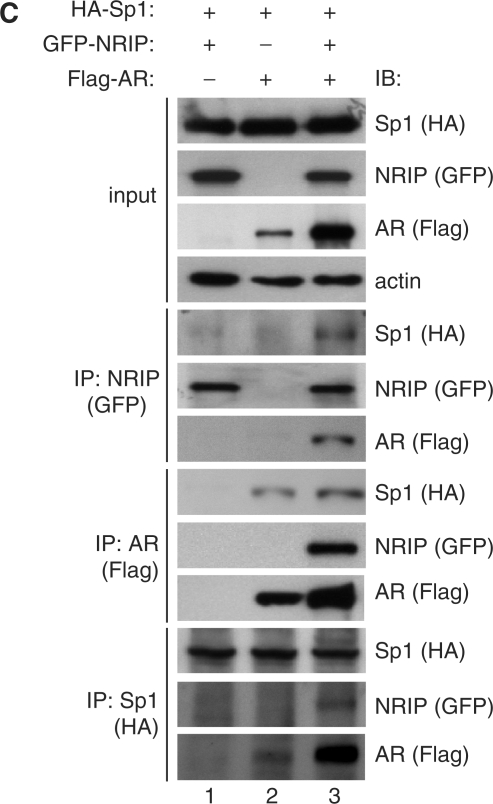
Figure 4.
AR and Sp1 associate on the NRIP promoter. (A) The association of AR and Sp1 on the endogenous NRIP promoter in LNCaP cells. Left Panel: ChIP assays were performed in LNCaP cells using primers specific to ARE or Sp1-2-binding sites (as described in Materials and Methods section) to assess AR and Sp1 association with the NRIP promoter with or without DHT. The DNA–protein complexes were then immunoprecipitated by anti-Sp1 and anti-AR and IgG (a negative control) antibodies separately and then subjected to semi-quantitative PCR. rIgG and mIgG represent rat and mouse IgG, respectively. Right Panel: to investigate potential interactions between AR and Sp1 at the NRIP promoter, re-ChIP analysis was performed using the chromatin extracts of the DHT-treated LNCaP cells immunoprecipitated with either anti-AR or anti-Sp1 antibodies. Anti-AR immunoprecipitants and anti-Sp1 immunoprecipitants were re-immunoprecipitated with antibodies to Sp1 or AR, respectively. Then DNAs were extracted and subjected to PCR. (B) The interaction of AR and Sp1 on the ectopic NRIP promoter in 293T cells. 293T cells were transiently transfected with the indicated promoter mutant constructs, pSG5-HA-Sp1 and pcDNA3.0-AR in the presence of DHT. ChIP assays were analyzed by anti-AR and anti-Sp1. (C) Interactions of AR, Sp1 and NRIP. The plasmids pSIN-flag-AR, pSG5-HA-hSp1 and pEGFP-NRIP were co-transfected into 293T cells, which were cultured in FBS medium. After 48 h, cell lysates were collected and immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP, anti-Flag and anti-HA antibodies for NRIP, AR and Sp1, respectively. IP products were subjected to western blotting using antibodies as indicated.