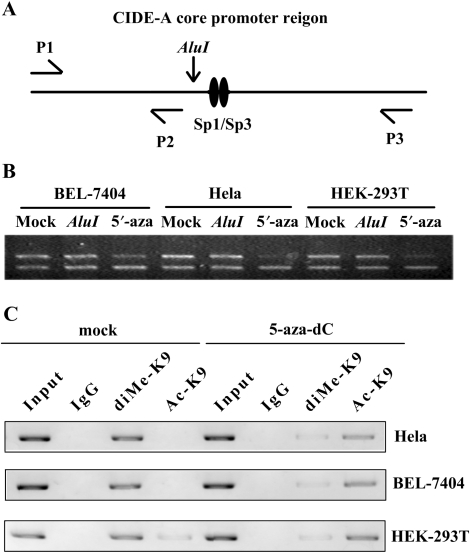
Figure 7.
5-aza-dC treatment changes the chromatin conformation around the CIDE-A promoter. (A) Procedure of nuclease accessibility assay. Nuclei were digested with the restriction enzyme AluI. DNA was extracted from the nuclei and amplified by PCR using a set of three primers (P1, P2 and P3). The decrease in the ratio 238:113 bp after AluI digestion indicates that the chromatin is accessible to AluI. (B) Chromatin accessibility changes in the critical CIDE-A promoter region in Hela, HEK-293T and BEL-7404 cells following treatment with 5-aza-dC. The ratio decreased significantly after treating with 1 M 5-aza-dC for 3 days. (C) In vivo H3K9 di-methylation and acetylation levels in the CIDE-A core promoter before and after 3 days’ 1 M 5-aza-dC treatment were analysed by Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay using antibodies that recognize Ac-H3K9 and di-methyl H3K9. The normal rabbit IgG was used as a negative control and Input indicates 5% input DNA, a positive amplification control.