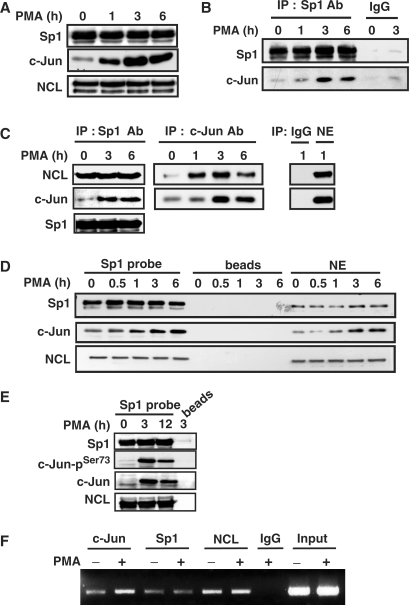
Figure 4.
PMA induces the complex formation and the binding of c-Jun, nucleolin and Sp1 to cPLA2α gene promoter in A549 cells. (A) Cells were starved for 18 h in serum-free culture medium and then treated with 5 nM PMA for a different time period as indicated. The Sp1, nucleolin (NCL) and c-Jun proteins were detected by anti-Sp1, anti-nucleolin and anti-c-Jun antibodies, respectively. (B and C) Nuclear extracts were immunoprecipitated (IP) with antibodies (Ab) against Sp1 and c-Jun. The proteins were subjected to SDS–PAGE and analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against c-Jun, NCL and Sp1. IgG: negative control of antibodies. (D and E) Cells were starved for 18 h in serum-free culture medium and then treated with 5 nM PMA for a different time period as indicated. Nuclear extracts were prepared and DNA affinity precipitation assay was performed as described under Materials and Methods section. Binding of Sp1, NCL, c-Jun and phospho-c-Jun (Ser73) to Sp1 probes were analyzed by western blot. The streptavidin-agarose beads were used to serve as a nonspecific binding control. (F) Cross-linked chromatin derived from PMA-treated cells was immunoprecipitated with c-Jun, NCL and Sp1 antibodies and analyzed by PCR with specific primers for the region from −239 to +19 bp of cPLA2α promoter. Input: nonimmunoprecipitated cross-linked chromatin.