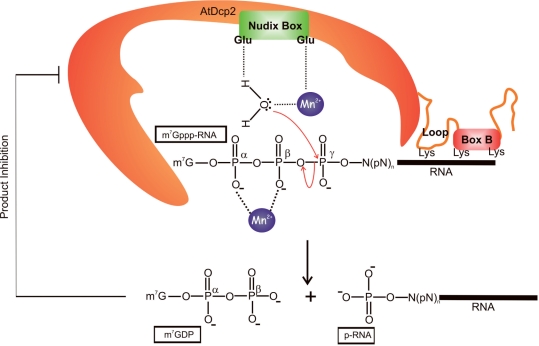
Figure 8.
A model of the catalytic mechanism, regulatory domains and regulatory properties of AtDcp2. Based upon the structure of the yeast Dcp2 and the results shown in Figure 6, we postulate that the two conserved glutamates in the Nudix box in AtDcp2 are catalytically critical residues. Hydrolysis of capped mRNA (m7-Gppp-RNA) involves nucleophilic attack of the γ-phosphate of m7-Gppp-RNA by a water molecule. The enhanced nucleophilicity and proper alignment of this water molecule are governed by electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding with a divalent cation (Mn2+) and one of the glutamates in the Nudix box. The second conserved glutamate in the Nudix box is involved in chelating the divalent cation. In addition, a second divalent cation is involved in binding the α- and β-phosphates of the substrate. The RNA moiety of m7-Gppp-RNA interacts with Box B and the preceding loop structure (KH-like motif). Lys-231 of the loop structure, and Lys-243 and Lys-248 of Box B are the likely determinants involved in binding RNA.