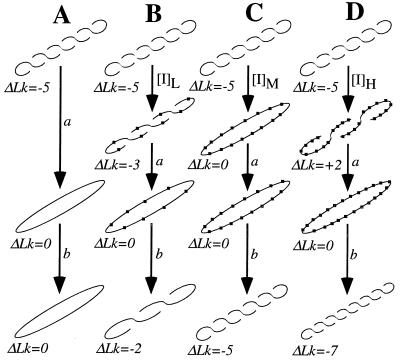
Figure 1.
Schematic Topo I relaxation reactions of ccDNA at no, low ([I]L), medium ([I]M), and high ([I]H) ligand binding. a, Topo I relaxation; b, ligand removal by organic extraction. Ligand molecules are represented as nodules along the helical axis of the ccDNA shown. Reaction A lacks ligand, so the ccDNA product is fully relaxed with ΔLk = 0. In reaction B, enough ligand is bound to titrate out 2 superhelical turns (sht) so that the ccDNA now contains −3 sht. After a and b, these 2 titrated sht are manifested in a final ΔLk of −2. Reaction C depicts just enough bound ligand to fully titrate all 5 sht, so product and starting ccDNAs are indistinguishable. Finally, D shows high-ligand binding to +2 sht beyond the equivalence point of C. In this example, the ccDNA product bears this additional superhelicity in its ΔLk of −7.