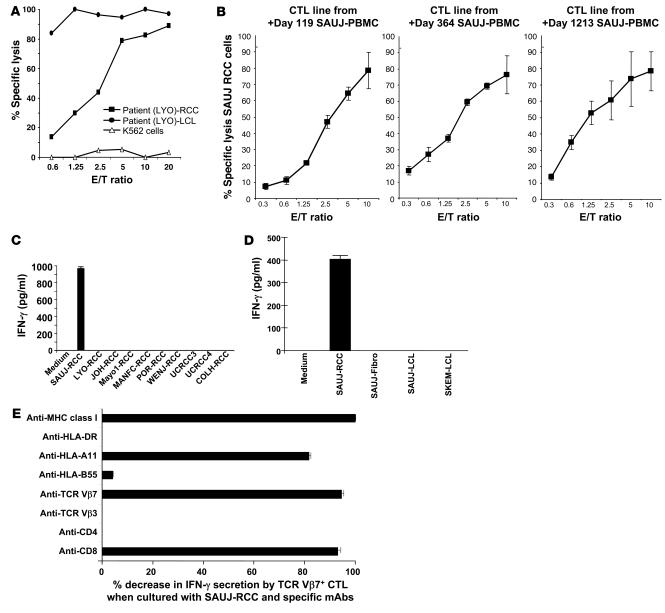
Figure 4. Detection of RCC-reactive CD8+ T cells in PBMCs after transplantation.
(A) A CTL line was expanded from RCC patient LYO by stimulating posttransplant day +211 PBMCs collected following tumor regression with irradiated LYO-RCC cells. Following limiting dilution cloning, an HLA class I–restricted CD8+ T cell clone (LYO-clone 1) was isolated that was highly cytotoxic to both patient autologous LCL and RCC cells. (B) CTL lines were expanded from patient SAUJ by stimulating PBMCs collected on post-HSCT days +119, +364, and +1,213 with irradiated SAUJ-RCC cells; expanded CTLs from all 3 time points were highly cytotoxic to SAUJ-RCC cells. (C) An ELISA showed that day +1,213 SAUJ-CTLs secreted IFN-γ when cultured with SAUJ-RCC cells but not with third-party HLA-mismatched RCC cell lines. (D) An ELISA assay measuring IFN-γ secretion showed that flow-sorted TCR-Vβ7+ SAUJ-CTLs recognized SAUJ-RCC cells but not patient SAUJ-LCL or donor SKEM-LCL cells or fibroblasts (SAUJ-Fibro). (E) Coculture of SAUJ-RCC cells with TCR-Vβ7+ SAUJ-CTLs. IFN-γ secretion by ELISA decreased substantially when SAUJ-CTLs were pretreated with either anti-CD8 or anti–TCR-Vβ7 mAbs or when SAUJ-CTLs were cocultured with SAUJ-RCC cells in the presence of anti–HLA class I or anti–HLA-A11 mAbs.