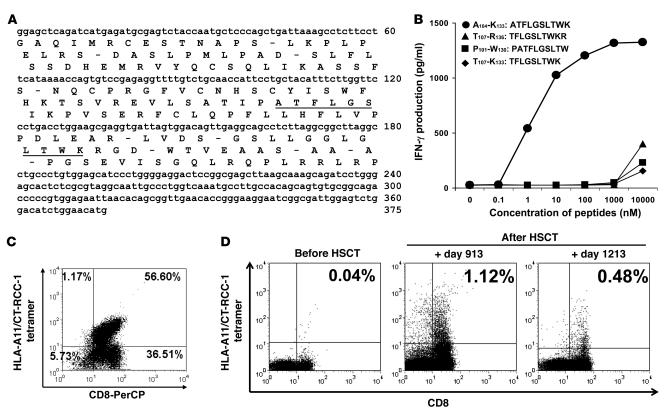
Figure 6. Identification of the peptide recognized by CTL expanded from a responding patient and detection of circulating CT-RCC-1 peptide–specific T cells after HSCT.
A 10-amino-acid HERV-E–derived peptide (CT-RCC-1) expressed on RCC was identified to be the target antigen of tumor-reactive CTL. (A) The position of the peptide was identified to be located in frame 2 of the 375-bp CT-RCC common region. (B) Four candidate peptides were synthesized from the predicted amino acid translations of these minigenes; only the 10-mer peptide ATFLGSLTWK induced dose-dependent IFN-γ production by SAUJ-RCC–reactive CTLs. (C) RCC-reactive SAUJ-CTL was generated by stimulating SAUJ-PBMCs (day +1,213) with irradiated SAUJ-RCC cells followed by flow sorting for TCR-Vβ7+CD8+ T cells. These CTLs were stained with a PE-conjugated HLA-A*1101/CT-RCC-1 (ATFLGSLTWK) tetramer; 56.6% of the CD3+CD8+ cells in this CTL line had antigen specificity for the CT-RCC-1 peptide. (D) PBMCs collected from SAUJ before HSCT did not bind to the CT-RCC-1 tetramer. CT-RCC-1–specific T cells were detected by tetramer analysis after HSCT in patient SAUJ on days +913 and +1,213 following tumor regression, constituting 1.12% and 0.48% of the CD3+CD8+ T cell repertoire, respectively.