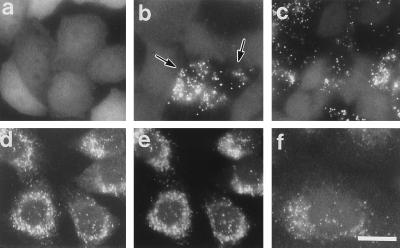
Figure 1.
Complementation of peroxisomes in CG-I CHO mutant cells. (a–c) Intracellular location of EGFP in ZP107EG1 cells, ZP107 stably expressing EGFP-PTS1, was monitored on unfixed cells grown on a coverslip, under a fluorescence microscope. (d–f) Immunofluorescent staining of peroxisomes in 107P1 cells, stable HsPEX1-transformants of ZP107. (a) Peroxisome-deficient mutant ZP107EG1 cells. (b) Peroxisome-restored ZP107EG1, after lipofection with a subpool (F6-17) of human cDNA library. Arrows indicate the complemented cells. Cytosolic appearance of EGFP-PTS1 was apparent in the other cells. (c) ZP107EG1 transfected with pUcD2Hyg⋅HsPEX1 plasmid. (d and e) 107P1 cells were stained with goat antibody to rat catalase plus donkey antibody to goat IgG conjugated to rhodamine (Chemicon) and antibody to PMP70, respectively. Note that punctate structures (peroxisomes) stained in d and e are superimposable. (f) 107P1 cells stained with antibody to 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase. (×630; bar = 20 μm.)