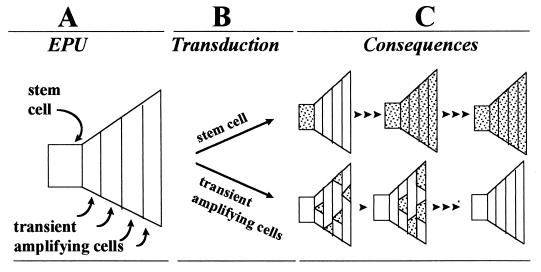
Figure 3.
Consequences of transduction of stem cells and transient amplifying cells. (A) EPU is illustrated by a polygonal figure. The stem cell is a square located at the left side of the polygon and sequential cycles of transient amplifying cells are depicted by areas that expand to the right. Terminal differentiation is not shown in the figure, but would occur after the last round of amplification division. (B) When an EPU is infected with a retrovirus, the stem cell or transient amplifying cells are transduced depending on the position of each in the cell cycle. (C) Transduced cells and their progeny are noted by shaded areas. Cell replication is indicated by an arrowhead. When the stem cell is transduced, all cells in the EPU become and remain labeled with repeated cycles of cell replication (Upper). When transient amplifying cells are transduced, there is an initial rise in the number of transgene-positive cells; however, with further replication, the EPU becomes depleted of transduced cells (Lower).