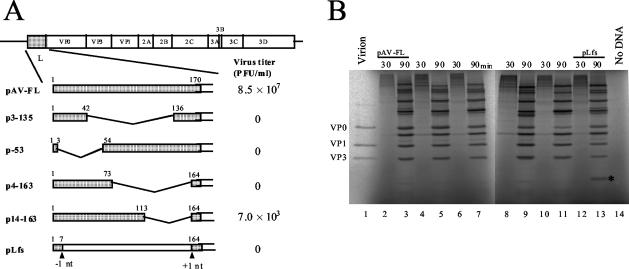
FIG. 4.
(A) Schematic diagrams of pAV-FL and the L mutants and their abilities to produce viable viruses. The open boxes and lines indicate coding and noncoding regions, respectively. Vertical lines within the box represent putative cleavage sites for viral proteinase. L protein sequences are shaded, and deleted regions are represented by angled lines. Amino acid numbers are indicated above the boxes. In pLfs, the positions where a nucleotide was deleted (−1 nt) and added (+1 nt) are indicated. RNA transcripts synthesized from these plasmids were transfected into Vero cells by lipofection, and the virus titers in the cells 72 h after transfection were determined by plaque assay. The number of plaques was determined 72 h after infection. (B) In vitro transcription-translation of pAV-FL and the L mutants in RRL. The plasmids were reacted in an in vitro transcription-translation system in the presence of [35S]methionine-cysteine for 30 or 90 min at 30°C. The translation products were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and the gel was dried. Radioactive signals were detected with a phosphorimager. To show the mobility of capsid proteins, 35S-labeled virions were analyzed. The asterisk indicates the unique protein produced from pLfs.