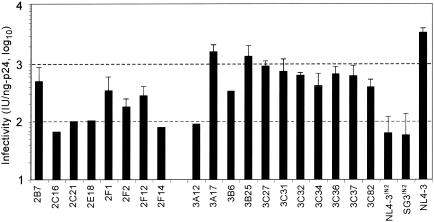
FIG. 3.
Analysis of a 5′ subgenomic DNA fragment derived from culture-adapted virus. SupT1 cells were infected with the CF-65 or CF-131 virus, and 2 days later high-molecular-weight DNA extracts were prepared. A 5.3-kb DNA fragment was amplified from each DNA extract by PCR and ligated into a pNL4-3 proviral backbone, from which multiple clones were derived. Then 6 μg of DNA of each clone was transfected into 293T cells by calcium phosphate DNA precipitation. The pNL4-3IN2, pSG3IN2, and pNL4-3 clones were included as controls. The culture supernatants were collected 48 h later and analyzed for HIV-1 p24 antigen concentration by ELISA and for infectivity with TZM-bl reporter cells. Infectivity is expressed by standardization to 1 ng of p24 antigen. The four most infectious clones derived from CF-65 (2B7, 2F1, 2F2, and 2F12) and the nine most infectious clones derived from CF-131 (3A17, 3B25, 3C27, 3C31, 3C32, 3C34, 3C36, 3C37, and 3C82) were analyzed in three separate experiments, and standard deviations were calculated.