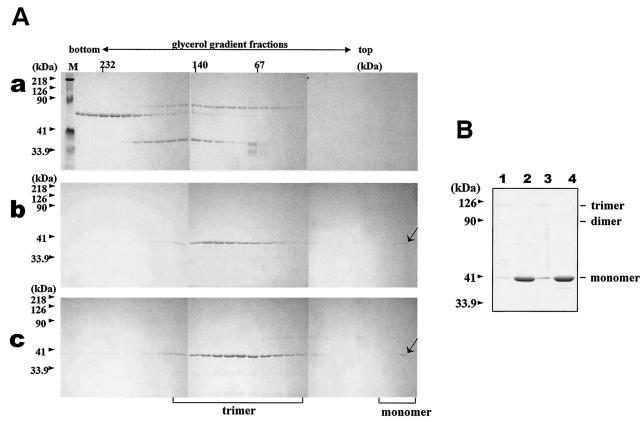
FIG. 6.
Trimerization assay of the wild-type and mutated BTV-10 VP7. Recombinant wild-type and mutant N38D VP7 was purified and assayed for trimer formation as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Sedimentation profiles of soluble VP7 protein on glycerol gradients. After purification, soluble VP7 mutants were subjected to velocity sedimentation analysis on 15 to 30% glycerol gradients to separate VP7 trimers. Fractions from the bottom to the top (left to right) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. An arrow marks the position of VP7. (a) High-molecular-weight calibration markers (in kilodaltons), catalase (4 × 58 kDa = 232 kDa), lactate dehydrogenase (4 × 36 kDa = 140 kDa), and serum albumin (67 kDa); (b) wild-type VP7; (c) mutant N38D VP7. Lane M shows molecular weight markers (Bio-Rad) for SDS-PAGE. (B) Coomassie blue-stained SDS-PAGE profiles of wild-type (lanes 1 and 2) and N38D VP7 samples (lanes 2 and 4) either boiled at 100°C for 5 min or incubated at 37°C for 5 min (lanes 1 and 3) prior to SDS-PAGE analysis. The positions of the VP7 monomer, dimer, and trimer are indicated.