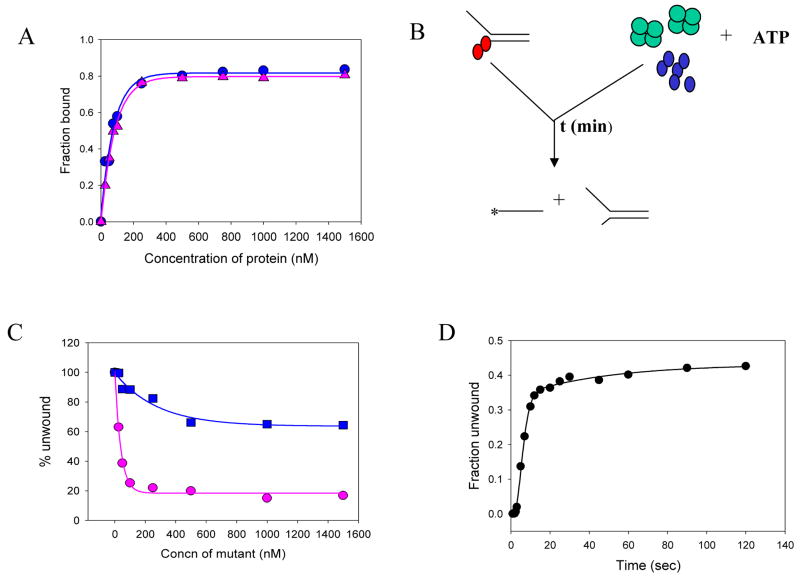
Fig. 5.
Mechanism of SSB action - mutant poisoning experiments. (A) Wild-type NS3h ( ) and mutant D261A NS3h ( ) bind to single-stranded DNA (Table I, 6) with equal affinity as assessed by the nitrocellulose filter binding assays. 20nM of 25mer DNA was incubated with increasing concentrations of either WT-NS3h or mutant D261A NS3h for 30 min at room temperature. The fraction of protein bound was plotted as a function of protein concentration. (B) Schematic representation of the unwinding experiments done in the presence of the mutant D261A. The red circles represent the WT NS3h, while the blue circles (on the right) represent the mutant D261A. The green tetramer represents the SSB protein. In the mutant poisoning experiments, The wild-type enzyme is pre-incubated with the DNA substrate and the reaction is initiated with the SSB-mutant NS3h-ATP mixture. The reaction is then quenched with SDS-EDTA quenching solution after appropriate times. (C) The unwinding of the 40bp substrate was measured using a constant amount of WT NS3h (100 nM) and increasing amounts of the mutant NS3h in the absence ( ) or in the presence of SSB ( ). 5nM forked substrate was pre-incubated with 200nM WT-NS3h. The unwinding reaction was initiated by mixing with equal volume of 10mM ATP and increasing concentrations of mutant D261A, either in the presence or absence of 1μM E.coli SSB. The amount of products formed in each case was plotted as a function of increasing mutant concentration. (D) The kinetics of 40bp substrate unwinding by NS3h in the presence of SSB and excess of the mutant D261A. WT-NS3h (200nM) was incubated with 5 nM ss/dsNA substrate in buffer in one syringe, and mixed with equal volume of 10 mM ATP, 2μM E.coli SSB and 1μM mutant NS3h D261A, in the same buffer from the other syringe for the times indicated. About 40% of the substrate is unwound at a rate of 3.9 bp/s.