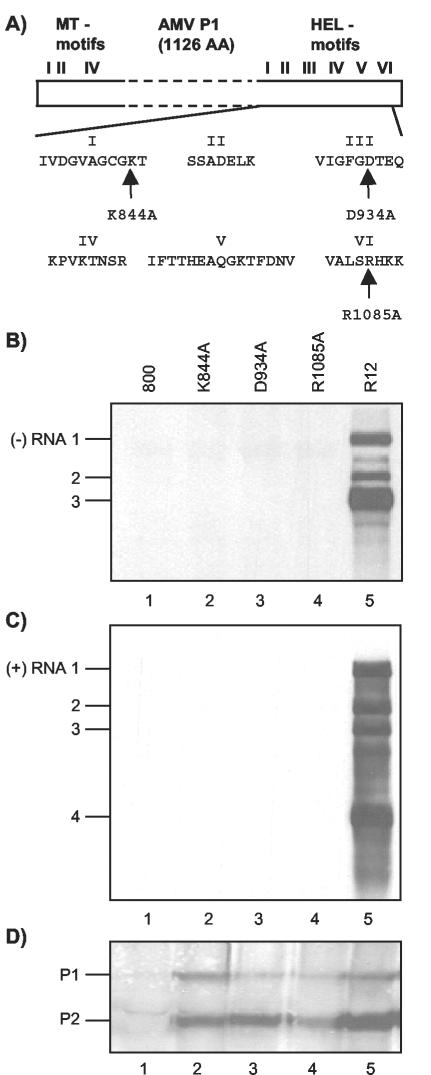
FIG. 1.
Mutations in RNA 1 affecting P1 helicase motifs interfere with viral RNA synthesis. (A) Schematic representation of P1 with N-terminal methyltransferase domain (MT) motifs and C-terminal helicase domain (HEL) motifs. The amino acids from helicase domain motifs I, III, and VI that are changed into alanine in mutants K844A, D934A, and R1085A, respectively, are indicated. (B to D) Analysis of the accumulation of viral negative-strand (−) RNAs (B), positive-strand (+) RNAs (C), and replicase proteins (D) in leaves infiltrated with a mixture of bacteria containing R12 and R3 constructs. The R3 construct expressed wt RNA 3 (lanes 1 to 5). The R12 construct expressed wt RNA 2 (lanes 2 to 5) and wt RNA 1 (lane 5) or RNA 1 encoding P1 with mutations in the helicase domain, as indicated above the lanes (lanes 2, 3, and 4). In leaves from which extracts were analyzed in lanes 1, the bacteria containing the R12 construct were replaced by bacteria containing the empty vector pMOG800 (800).Protein and RNA were extracted from the leaves 2 and 5 days p.i., respectively. RNA was analyzed by Northern blot hybridization using strand-specific probes (B and C). Protein was analyzed by Western blotting using antisera raised against P1 and P2 (D). The positions of RNAs 1, 2, 3, and 4 and proteins P1 and P2 are indicated on the left.