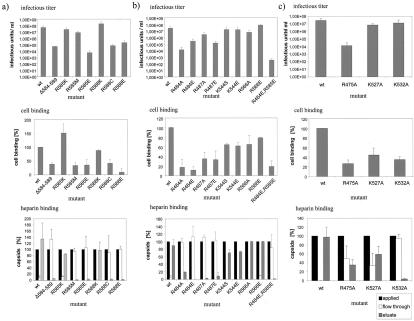
FIG. 2.
Influence of mutations of basic amino acids in loop IV on infectivity, cell binding, and heparin binding of AAV-2. Virus stocks were produced by transfection of wild-type (wt) or mutated AAV-2 genomic plasmids into 293T cells and superinfection with adenovirus (multiplicity of infection, 50). (a) Analysis of arginines 585 and 588 for involvement in heparin binding. (b) Analysis of distantly located basic amino acids predicted to possibly contribute to heparin binding. (c) Further loop IV basic amino acids involved in heparin binding. Infectious units were determined as described in Materials and Methods. Capsid titers and genomic titers were not influenced by the mutations (data not shown), implying that they did not affect capsid assembly or genome encapsidation. Virus bound to HeLa cells was measured with monoclonal antibody A20 (68). Heparin binding was assayed by chromatography of virus preparations (freeze-thaw lysates) with heparin-agarose and quantitation of applied, flowthrough, and salt-eluted virus with the A20 capsid ELISA. The amount of applied virus was set to 100%. Error bars indicate standard deviations of at least three independent experiments.