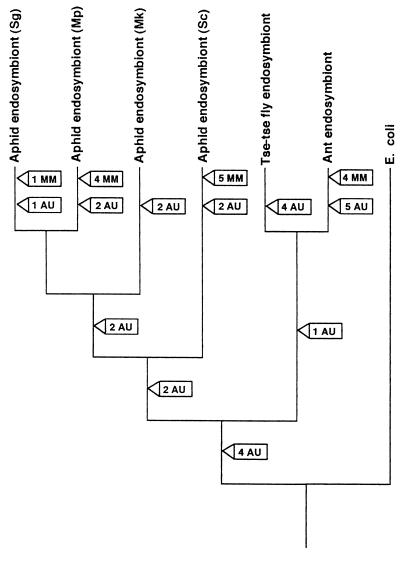
Figure 3.
Positions of destabilizing substitutions of endosymbionts related to E. coli, assuming both the tree topology and the mapping of substitutions that minimize independent events. Destabilizing substitutions are divided into two categories, those causing a stem mismatch (MM) and those causing an AU or GU pair to replace a GC pair in a stem (AU). Where two substitutions are associated with an event in either category (e.g., an AU pair replaces a GC pair), only one destabilization event is mapped onto the tree. Even with these assumptions, which minimize independent events, most destabilizing substitutions are unique to individual lineages, indicating largely independent evolution of destabilization.