Figure 2.
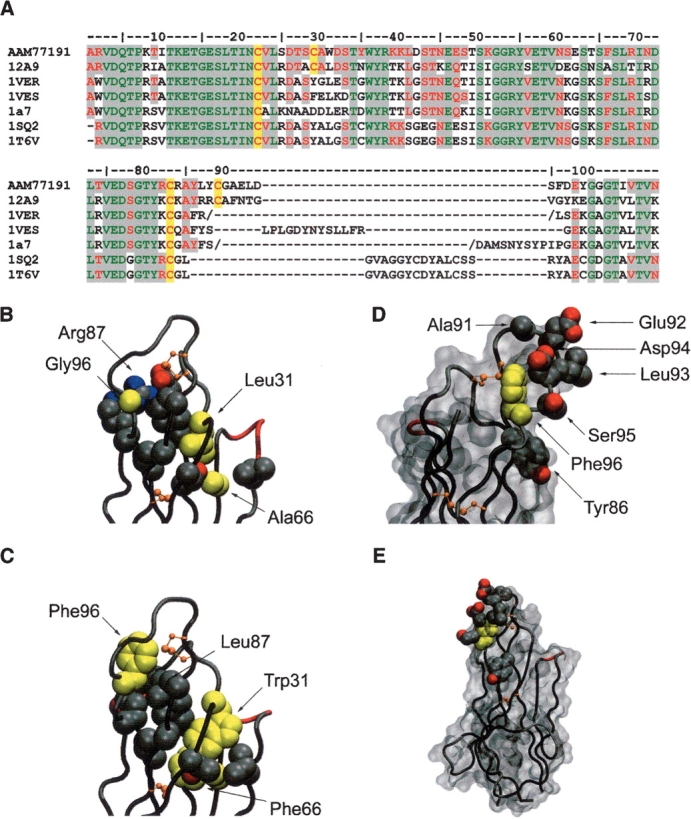
Modeling of the Type 3 IgNAR antibody isotype. (A) Sequence alignment of Type 3 VNAR AAM77191 with structural templates used for modeling. The conserved Ig superfamily framework cysteine residues and those found in the Type 2 and Type 3 CDR3 loop regions are highlighted in yellow. Regions of sequence homology are highlighted in gray (green, residues identical in all known VNAR structures and AAM77191; red, residues conserved in all known VNAR structures and AAM77191). (B) The 12A-9 CDR loops shown in Cα tube representation. Side-chain atoms of residues involved in packing of the hydrophobic core supporting these loops are shown as cpk balls. Modeled residue side chains for Leu31/Trp31 and Gly96/Phe96 (as well as Ala66/Phe66) are shown in yellow. (C) Predicted model of the Type 3 loop in the same representation as for B. (D) Predicted model of the Type 3 CDR3 loop showing the conserved central hydrophobic Phe96 residue in yellow, surrounded by variable residues putatively involved in antigen binding shown as side-chain atoms rendered as cpk balls. A solvent accessible surface is also shown in gray, orientation ~170° rotation in the vertical axis. (E) Same as for D, but in the same orientation as C, and illustrating the relatively small surface area occupied by the hypervariable residues in the context of the complete single domain antibody. Diagrams were constructed in VMD (Humphrey et al. 1996).
