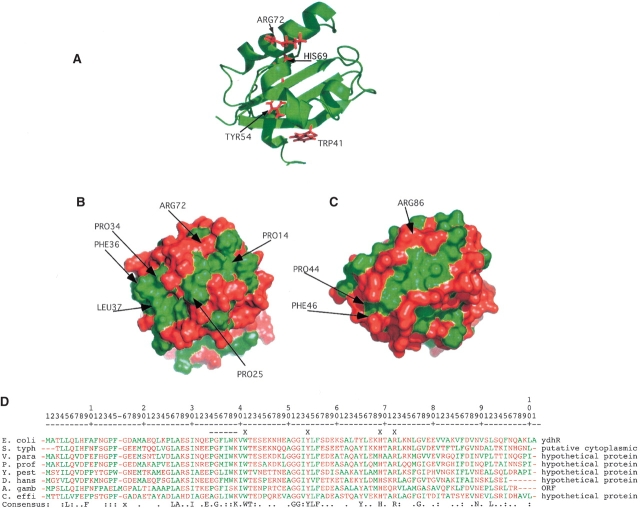
Figure 2.
Structure of the hydrophobic cleft and possible active site residues. (A) Ribbon structure of ydhR oriented to exhibit the conserved residues in the cleft that correspond to conserved residues in the active site of ActVA-Orf6 that interact with substrate. (B) Surface model of ydhR oriented identically to A colored green for hydrophobic amino acids (Ala, Leu, Ile, Phe, Met, Val, Trp) and red for all other amino acids. The green, hydrophobic cleft is clearly visible on the front face of the surface. (C) Surface model of ActVa-Orf6 (PDB: 1LQ9) with the active cleft oriented similarly to that of the ydhR structure. The hydrophobic nature of the active site of ActVa-Orf6 corresponds closely to that of ydhR. (D) BLAST alignment of bacterial protein sequences most similar to ydhR. None of these proteins has a defined structure or function. S. typh, Salmonella typhimurium; V. para, Vibrio parahaemolyticus; P. prof, Photobacterium profundum; Y. pest, Yersinia pestis; D. hans, Debaryomyces hanseii (yeast); A. gamb, Anopheles gambiae (insect); C. effi, Corynebacterium efficiens. Hydrophobic residues are colored green as in B and all other residues are colored red. An X on the line above the alignment indicates the residues highlighted in A, and the dashed line indicates the conserved PGFL sequence in ActVa-Orf6. The bottom consensus line indicates completely conserved residues, a colon indicates residues conserved in seven out of eight of the sequences; a period indicates positions occupied by either polar or hydrophobic residues in at least seven of the eight sequences.