Figure 5.
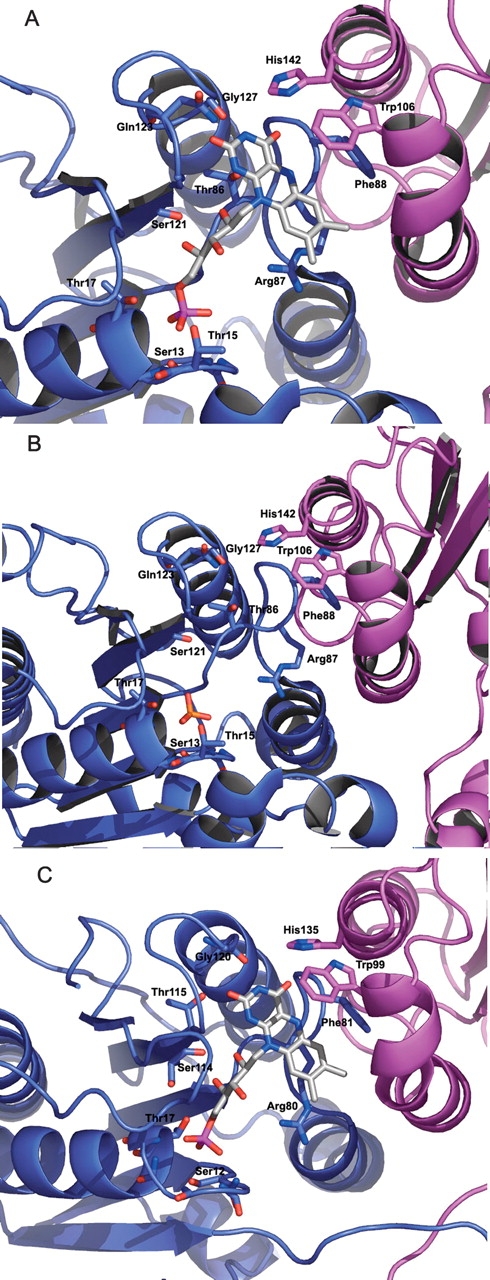
(A) FMN binding site of WrbA from D. radiodurans. The phosphate moiety shows interactions with a number of residues in the loop following β1. Note the side-chain interactions of Ser13 and Thr17, which are conserved in many flavodoxins. His142 from a tetramermate chain interacts with the isoalloxazine ring, thus also contributing to FMN binding. (B) The FMN binding site of WrbA from D. radiodurans crystallized in the presence of sulfate and the absence of FMN. The sulfate binds to the location where the phosphate moiety of FMN is found in the complex. (C) FMN binding site of WrbA from P. aeruginosa. The site is similar to that of D. radiodurans, despite some sequence divergence in the loop following β1. The isoalloxazine ring is similarly stacked around Arg80, Phe81, and Trp99. The FMN also interacts with His135 of a second tetramermate chain.
