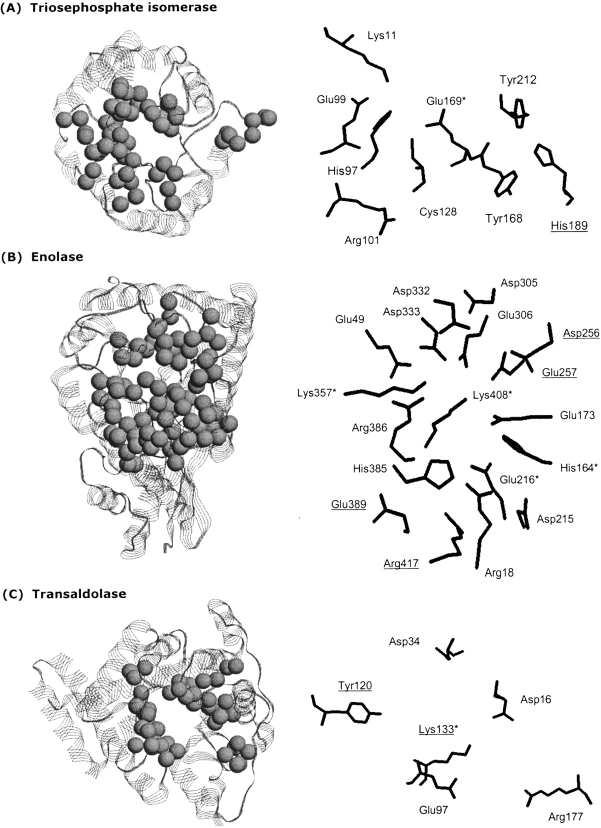
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic motifs (left) and electrostatic networks (right) of (A) triosephosphate isomerase, (B) enolase, and (C) transaldolase. (Left) Spheres represent phylogenetic motif α-carbons. In all cases, the identified phylogenetic motifs are structurally clustered at the C-terminal end of the barrel. (Right) All residues implicated in the functional electrostatic networks are indicated. Positions included here are based on a simple majority from the multiple sequence alignments in Figure 5 ▶. Catalytic residues are indicated by an asterisk; nonphylogenetic motif residues are underlined. For example, the catalytic residue of transaldolase (Lys133) is not part of any identified phylogenetic motif. Residue numbering is the same as in Figure 4 ▶.