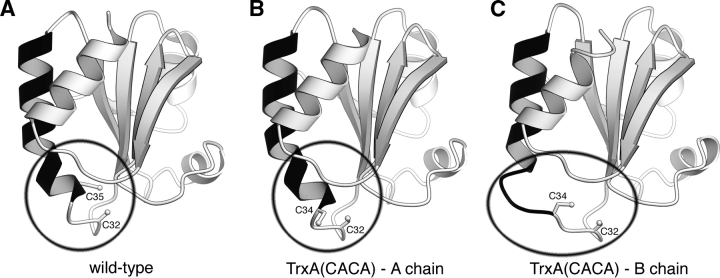
Figure 2.
The unraveling active site. Three ribbon renderings of TrxA monomers. An extended helix (residues 34–50) is colored black. (A) The structure of the wild-type TrxA (PDB accession code 1XOB). (B) The A chain of TrxA(CACA). (C) The B chain of TrxA(CACA). The A chain of the TrxA(CACA) dimer has nearly identical structure to the wild-type form. In the B chain, the beginning of the black extended helix has unraveled to allow the disulfide bond formation. Note that in the wild-type enzyme, only one cysteine (Cys32) is accessible to the solvent, whereas in Trx(CACA) two cysteines (Cys32 and Cys34) are accessible.