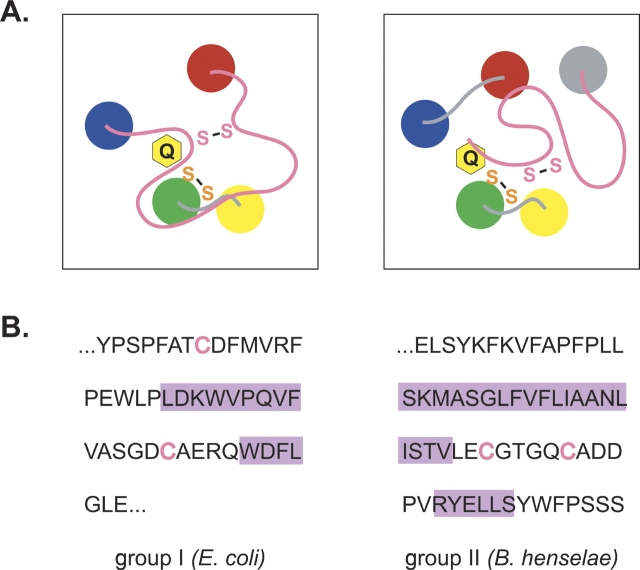
Figure 6.
(A) Diagram of the proposed active site of the group I (left) and group II (right) DsbB proteins. The transmembrane helices of DsbB are drawn as colored circles. The Cys-x-x-Cys active site and the second conserved cysteine pair are represented as an orange or pink “S-S,” respectively, and a yellow ring labeled Q represents the quinone cofactor. (B) DsbB amino acid sequence connecting helices D and C in the group I proteins, or forming the C-terminal domain of the group II proteins. The E. coli and B. henselae DsbB proteins were arbitrarily chosen as representative of the group I and group II proteins, respectively. Cysteines are represented in pink text, while purple rectangles highlight residues predicted to form helices by the PSIPRED program (Jones 1999; McGuffin et al. 2000). The nonhighlighted sequence is predicted to adopt a conformation differing from canonical secondary structures (α-helix and β-sheet).